Beyond M1/M2: CD38/Egr2 Flow Cytometry Reveals New Macrophage Polarization Paradigms for Immunotherapy
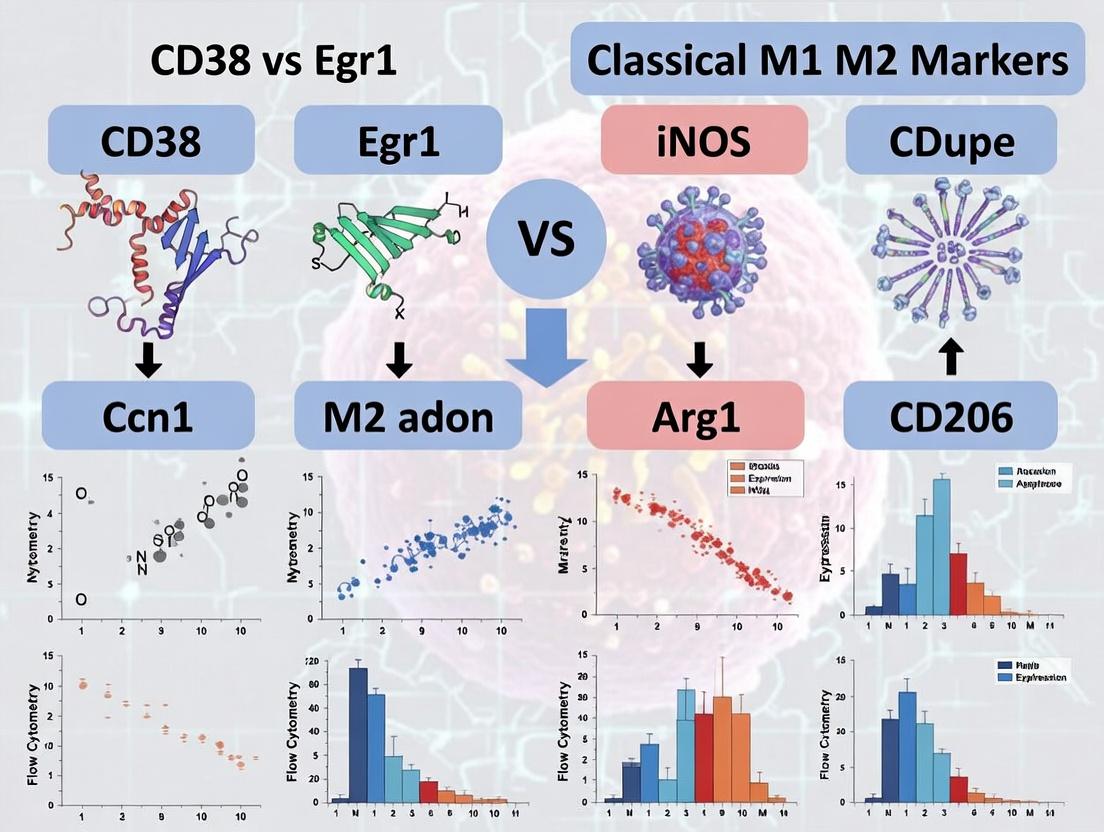
This article provides a comprehensive guide for researchers comparing novel (CD38, Egr2) and classical (iNOS, Arg1, CD206) macrophage polarization markers in flow cytometry.
Beyond M1/M2: CD38/Egr2 Flow Cytometry Reveals New Macrophage Polarization Paradigms for Immunotherapy
Abstract
This article provides a comprehensive guide for researchers comparing novel (CD38, Egr2) and classical (iNOS, Arg1, CD206) macrophage polarization markers in flow cytometry. Moving beyond the simplistic M1/M2 dichotomy, we explore the foundational biology of these markers, detailing optimized staining protocols, multi-panel design, and critical gating strategies. We address common troubleshooting pitfalls in detecting intracellular and surface antigens, and perform a rigorous validation and comparative analysis of marker specificity, dynamic expression, and functional correlation. This resource equips drug developers and immunologists with the methodological framework to accurately profile complex macrophage phenotypes in inflammation, cancer, and autoimmune disease models.
Deconstructing Macrophage Polarization: From Classical M1/M2 to Novel CD38/Egr2 Signaling Hubs
The Limitations of the Classical M1/M2 Dichotomy in Modern Immunology
The classical M1/M2 paradigm, which categorizes macrophages into pro-inflammatory (M1) and anti-inflammatory/reparative (M2) subsets based on markers like iNOS, Arg1, and CD206, has provided a foundational framework for immunology. However, modern research, particularly in advanced models like CD38+ Egr2+ macrophages, reveals significant limitations of this binary view, demonstrating a spectrum of functional states that are context-dependent and plastic.
Comparative Performance: Classical Markers vs. Emerging Signatures
Table 1: Flow Cytometry Comparison of Classical M1/M2 vs. CD38/Egr2 Signatures
| Feature | Classical M1 (e.g., LPS/IFN-γ) | Classical M2 (e.g., IL-4/IL-13) | CD38+ Egr2+ Macrophages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Inducers | LPS, IFN-γ | IL-4, IL-13 | Immune complexes, TLR ligands, IL-10 |
| Surface Markers | CD80, CD86, MHC-II High | CD206, CD163, CD209 | CD38, FcgR, MHC-II Intermediate |
| Metabolic Enzyme | iNOS (NOS2) | Arginase-1 (Arg1) | CD38 (NADase) |
| Transcription Factor | STAT1, NF-κB, IRF5 | STAT6, IRF4, PPARγ | Egr2, c-Maf |
| Cytokine Profile | High TNF-α, IL-12, IL-1β, IL-6 | High IL-10, TGF-β, CCL17, CCL22 | High IL-10, IL-1RA, intermediate IL-12 |
| Functional Role | Pathogen killing, Th1 response, tissue damage | Tissue repair, immunoregulation, Th2 response, fibrosis | Regulatory, tissue homeostasis, suppression of inflammation |
| Limitations in Classification | Oversimplifies inflammatory response; misses heterogeneous states. | Fails to capture regulatory subtypes distinct from wound-healing. | Represents a unique regulatory state not described by M1/M2. |
Table 2: Experimental Data from Comparative Studies
| Study Model | M1 Metric (iNOS+ %) | M2 Metric (Arg1+ %) | CD38+Egr2+ % | Key Functional Readout |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peritonitis Model | 45-60% | 20-30% | 10-15% | CD38+ subset correlated with resolution phase, not acute inflammation. |
| Tumor-Associated Macrophages | 5-15% | 40-70% | 8-20% | CD38+Egr2+ population associated with poor response to anti-PD1 therapy. |
| Autoimmune Arthritis | 30-50% | 10-25% | 15-25% | Egr2+ cells increased post-immunosuppressive therapy, predictive of remission. |
| In Vitro LPS+IC Stimulation | 70% (iNOS mRNA) | 5% (Arg1 mRNA) | 65% (CD38 protein) | Co-expression of CD38 and iNOS challenges mutually exclusive paradigm. |
Detailed Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Polychromatic Flow Cytometry for Macrophage Phenotyping
- Cell Harvest & Preparation: Isolate macrophages from tissue via enzymatic digestion (Collagenase IV/DNase I) or harvest from in vitro culture.
- Fc Block: Incubate cells with anti-CD16/32 antibody (1:100) in FACS buffer (PBS + 2% FBS) for 10 minutes on ice.
- Surface Staining: Add antibody cocktail for surface markers. A typical panel includes: CD45 (hematopoietic lineage), F4/80 (macrophages), CD11b, MHC-II, CD38, CD206, CD86. Incubate for 30 minutes in the dark at 4°C. Wash twice.
- Fixation & Permeabilization: Fix cells with 4% PFA for 20 minutes. Wash, then permeabilize with ice-cold 90% methanol for 30 minutes on ice.
- Intracellular Staining: Wash twice in permeabilization buffer. Stain with antibodies against iNOS, Arg1, Egr2, and/or transcription factors for 60 minutes at room temp.
- Acquisition & Analysis: Acquire on a high-parameter flow cytometer (e.g., 5-laser). Analyze using sequential gating: single cells > live > CD45+ > F4/80+CD11b+ > then various marker combinations. Use fluorescence-minus-one (FMO) controls.
Protocol 2: In Vitro Generation of Macrophage Subsets for Comparison
- M1 Polarization: Differentiate bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) with M-CSF (20 ng/mL) for 7 days. Stimulate with 100 ng/mL LPS + 20 ng/mL IFN-γ for 18-24 hours.
- M2 Polarization: Differentiate BMDMs as above. Stimulate with 20 ng/mL IL-4 + 20 ng/mL IL-13 for 48 hours.
- Regulatory (CD38+Egr2+) Polarization: Differentiate BMDMs. Stimulate with immune complexes (IC) formed by incubating 10 µg/mL OVA with 5 µg/mL anti-OVA IgG for 1h) in combination with 10 ng/mL IL-10 or a low dose of LPS (1 ng/mL) for 48 hours.
Visualizing Macrophage Activation Pathways
Macrophage Activation Pathways & Markers
Flow Cytometry Gating Strategy for Subsets
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Reagents for Macrophage Polarization & Analysis
| Reagent | Supplier Examples | Function in Experiment |
|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Murine M-CSF | BioLegend, PeproTech | Differentiates bone marrow precursors into resting macrophages (BMDMs). |
| Polarizing Cytokines (LPS, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-13) | R&D Systems, Invitrogen | Used to induce classical M1 or M2 polarization states in vitro. |
| Anti-CD16/32 (Fc Block) | Tonbo Biosciences, BioLegend | Blocks non-specific antibody binding via Fc receptors, critical for clear flow cytometry. |
| Fluorochrome-conjugated Antibodies (CD45, F4/80, CD11b, CD38, CD206, MHC-II) | BD Biosciences, BioLegend, Invitrogen | Surface staining for identifying cell lineage and activation markers. |
| Intracellular Staining Antibodies (iNOS, Arg1, Egr2) | Cell Signaling Technology, Novus Biologicals | Detects key functional and transcriptional markers inside permeabilized cells. |
| Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | Invitrogen, Tonbo Biosciences | Optimized buffers for fixing, permeabilizing, and staining nuclear antigens like Egr2. |
| Collagenase Type IV & DNase I | Worthington Biochem, Sigma-Aldrich | Enzyme cocktail for gentle dissociation of macrophages from solid tissues. |
| High-Parameter Flow Cytometer (e.g., Aurora, Fortessa X50) | Cytek, BD Biosciences | Instrument capable of detecting 20+ colors, necessary for complex phenotyping. |
Within macrophage biology, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and Arginase-1 (Arg1) have served as definitive functional markers for the classical M1 (pro-inflammatory) and M2 (alternatively activated/anti-inflammatory) polarization states, respectively. This comparison guide objectively evaluates their performance as polarization markers in the context of modern flow cytometry, particularly against emerging paradigms like the CD38/Egr2 axis and the classical CD206 marker. The analysis is framed within a broader thesis re-evaluating M1/M2 classification, incorporating the latest research data.
Quantitative Comparison of Macrophage Polarization Markers
Table 1: Functional and Phenotypic Characteristics of Key Polarization Markers
| Marker | Primary Polarization State | Enzymatic Function / Role | Key Cytokine Inducers | Typical Flow Cytometry Signal Intensity (MFI Ratio vs. Control) | Specificity for Human vs. Mouse | Correlation with Functional Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iNOS (NOS2) | Classical M1 | Converts L-arginine to nitric oxide (NO) and citrulline. NO mediates microbial killing and tissue damage. | IFN-γ + LPS, TNF-α | High (10-50x) in mouse; Often low/basal in human macrophages. | High in mouse models; Often less reliable as a primary M1 marker in human cells. | Strong correlation with NO production and bactericidal activity in mice. |
| Arginase-1 (Arg1) | Classical M2a | Hydrolyzes L-arginine to ornithine and urea. Ornithine contributes to polyamine and proline synthesis, promoting cell proliferation and tissue repair. | IL-4, IL-13 | Moderate to High (5-20x) | Expressed in both species, but regulation and prominence can differ. | Strong correlation with wound healing and pro-fibrotic functions. |
| CD38 | M1-like (Activation) | Ectoenzyme producing second messengers (cADPR, ADPR). Drives glycolytic metabolism and IFN-γ-mediated responses. | IFN-γ, TLR agonists | High (10-30x) | Robust marker in both human and mouse macrophages. | High correlation with inflammatory cytokine production (IL-6, TNF-α) and glycolytic flux. |
| Egr2 | M2-like (Early) | Transcription factor regulating genes involved in anti-inflammatory and pro-resolutive functions. | IL-4, IL-13 (transient early induction) | Nuclear protein; requires intracellular staining. Measurable shift. | Conserved role in both species. | Correlates with a subset of IL-4-induced genes, distinct from Arg1-high populations. |
| CD206 (MMR) | Classical M2 | Mannose receptor; phagocytosis and endocytosis of glycoproteins. | IL-4, IL-13, glucocorticoids | High surface expression (10-100x) | Excellent, consistent pan-M2 marker in both human and mouse. | Correlates with scavenging and endocytic activity, not always with Arg1 activity. |
Table 2: Experimental Comparison in a Model Polarization Study (Hypothetical Data Based on Current Literature)
| Experimental Readout | M1 (IFN-γ + LPS) | M2 (IL-4) | Assay Method | Notes & Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| iNOS Protein (MFI) | 4500 ± 520 | 150 ± 30 | Intracellular Flow Cytometry | Definitive for murine M1. |
| Arg1 Protein (MFI) | 200 ± 45 | 3800 ± 610 | Intracellular Flow Cytometry | Definitive for M2a. |
| NO (nitrite, µM) | 42.5 ± 5.1 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | Griess Assay | Functional correlate of iNOS. |
| Urea (mM) | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 8.5 ± 1.2 | Colorimetric Assay | Functional correlate of Arg1. |
| CD38 Surface (MFI) | 12500 ± 1500 | 800 ± 200 | Surface Flow Cytometry | More sensitive than iNOS for human inflammatory macrophages. |
| Egr2 mRNA (Fold Change) | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 15.2 ± 2.8 | qRT-PCR | Early transient marker. |
| CD206 Surface (MFI) | 500 ± 100 | 25000 ± 3000 | Surface Flow Cytometry | Robust, stable surface M2 marker. |
Experimental Protocols for Key Comparisons
Protocol: Combined Flow Cytometry for iNOS/Arg1 and Surface Markers
Objective: Simultaneously quantify classical enzymatic and modern surface markers (CD38/CD206) in polarized bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). Materials: C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow, M-CSF, IFN-γ, LPS, IL-4, cell culture media, flow cytometry buffer (PBS + 2% FBS), fixation/permeabilization kit (e.g., Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set). Antibodies: Anti-mouse CD16/32 (Fc block), BV785 anti-F4/80, APC anti-CD11b, PE anti-iNOS, Alexa Fluor 488 anti-Arg1, PE/Cy7 anti-CD38, PerCP/Cy5.5 anti-CD206, viability dye. Procedure:
- Differentiate & Polarize: Generate BMDMs with M-CSF (20 ng/mL) for 7 days. Polarize with IFN-γ (20 ng/mL) + LPS (100 ng/mL) for M1 or IL-4 (20 ng/mL) for M2 for 24 hours.
- Harvest & Stain Surface Antigens: Harvest cells, wash, and block Fc receptors. Stain with surface antibody cocktail (F4/80, CD11b, CD38, CD206) and viability dye for 30 min at 4°C.
- Fix & Permeabilize: Wash cells, then fix and permeabilize using the commercial kit per manufacturer's instructions.
- Stain Intracellular Antigens: Stain intracellularly with anti-iNOS and anti-Arg1 antibodies in permeabilization buffer for 45 min at room temperature.
- Acquire & Analyze: Wash, resuspend, and acquire data on a flow cytometer capable of detecting 8+ colors. Gate on live, single, F4/80+CD11b+ macrophages. Analyze median fluorescence intensity (MFI) for all markers.
Protocol: Functional Enzyme Activity Assays
A. Griess Assay for iNOS Activity (Nitrite Quantification)
- Sample Prep: Collect supernatant from polarized macrophages (e.g., from 3.1). Centrifuge to remove debris.
- Reaction: Mix 50 µL of sample with 50 µL of Griess Reagent (1% sulfanilamide, 0.1% NED in 2.5% phosphoric acid) in a 96-well plate.
- Incubation & Readout: Incubate at RT for 10 min protected from light. Measure absorbance at 540 nm. Calculate nitrite concentration from a standard curve of sodium nitrite.
B. Arginase Activity Assay (Urea Quantification)
- Lysate Prep: Lyse polarized macrophage cell pellets (1e6 cells) in 100 µL of 0.1% Triton X-100 with protease inhibitors. Activate arginase by adding 100 µL of 10 mM MnCl2 and heating at 56°C for 10 min.
- Enzymatic Reaction: Add 100 µL of 0.5 M L-arginine (pH 9.7) to the lysate. Incubate at 37°C for 60 min.
- Urea Detection: Stop reaction with 400 µL of acid stop mix (H2SO4:H3PO4:H2O = 1:3:7). Add 25 µL of 9% α-isonitrosopropiophenone (in ethanol), heat at 100°C for 45 min. Cool, protect from light, and read absorbance at 540 nm. Calculate urea from a standard curve.
Signaling Pathway and Workflow Visualizations
Diagram Title: iNOS vs. Arg1 in M1/M2 Polarization
Diagram Title: Flow Cytometry Gating for M1/M2 Analysis
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Reagents and Resources for Macrophage Polarization Studies
| Reagent / Material | Supplier Examples | Primary Function in iNOS/Arg1 Research |
|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Murine M-CSF | BioLegend, PeproTech | Differentiation of bone marrow progenitors into naive macrophages (BMDMs). |
| Polarizing Cytokines (mu/hu IFN-γ, IL-4, LPS) | R&D Systems, PeproTech, Sigma | Induce classical M1 (IFN-γ+LPS) and M2 (IL-4) polarization states. |
| Fluorochrome-conjugated Anti-iNOS Antibody | Thermo Fisher, BioLegend, BD Biosciences | Intracellular detection of iNOS protein by flow cytometry. Critical for murine M1 identification. |
| Fluorochrome-conjugated Anti-Arg1 Antibody | R&D Systems, Thermo Fisher, Cell Signaling Tech | Intracellular detection of Arg1 protein by flow cytometry. Standard marker for M2a. |
| Anti-CD38 (Clone 90) | BioLegend, BD Biosciences | Surface staining for the emerging M1-like activation marker (superior for human). |
| Anti-CD206 (MMR) | BioLegend, BD Biosciences | Surface staining for the classical and robust M2 marker. |
| Foxp3 / Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | Thermo Fisher, BioLegend | Permeabilization buffer optimized for intracellular staining of proteins like iNOS and Arg1. |
| Griess Reagent Kit | Thermo Fisher, Promega, Sigma | Colorimetric quantification of nitrite, the stable end product of iNOS activity. |
| Arginase Activity Assay Kit | Sigma-Aldrich, Abcam | Colorimetric quantification of urea produced by arginase enzyme activity. |
| L-NMMA (NOS inhibitor) or Nor-NOHA (Arg inhibitor) | Cayman Chemical, Sigma | Pharmacological tools to inhibit iNOS or arginase, respectively, for functional validation experiments. |
| Multicolor Flow Cytometer (e.g., Aurora, Cytek) | Cytek, BD, Beckman Coulter | High-parameter spectral or conventional cytometers essential for analyzing multiple markers simultaneously. |
CD206, also known as the mannose receptor C-type 1 (MRC1), is the canonical cell surface receptor defining the alternatively activated (M2) macrophage phenotype. Its expression is a cornerstone in immunometabolism and macrophage polarization research, often contrasted with markers for classically activated (M1) macrophages like iNOS (encoded by NOS2) and CD38. This guide compares CD206 as an M2 marker against other common alternatives, framed within the broader paradigm of macrophage polarization analysis, particularly in flow cytometry-based studies that dissect the CD38/Egr2 axis versus the classical iNOS/Arg1/CD206 (M1/M2) framework.
Comparative Performance of CD206 vs. Alternative M2 Markers
The identification of M2 macrophages relies on a panel of markers, as no single marker is universally exclusive. CD206 is a direct phagocytic pattern recognition receptor, while others like CD163, Arg1, and Ym1/2 are functional enzymes or scavenger receptors. Their expression can vary by tissue, species, and inflammatory context.
Table 1: Comparison of Canonical M2 Macrophage Markers
| Marker | Full Name | Primary Function | Expression Context | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD206 (MRC1) | Mannose Receptor C-type 1 | Phagocytosis, endocytosis of glycoproteins | Induced by IL-4/IL-13; Steroid hormones. | Canonical surface marker; ideal for flow cytometry & IHC. | Can be expressed on some dendritic cells; regulation can be complex. |
| CD163 | Scavenger Receptor Cysteine-Rich Type 1 | Hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex clearance | Induced by IL-10; glucocorticoids. | Highly specific for monocyte-macrophage lineage. | Shed as soluble form (sCD163) upon activation. |
| Arg1 | Arginase-1 | Hydrolyzes L-arginine to ornithine and urea. | Induced by IL-4/IL-13, IL-10. | Defines functional M2 metabolism (pro-polyamine/pro-collagen). | Intracellular enzyme; requires cell permeabilization for detection. |
| Ym1/2 (Chi3l3) | Chitinase-like protein 3 | Binds glycosaminoglycans (no enzymatic activity). | Highly induced by IL-4/IL-13 in mice. | Robust mouse M2 marker. | Not a direct homologue in humans (CHI3L1 is analogous). |
| FIZZ1 (Relmα) | Resistin-like molecule alpha | Unknown, may promote fibrosis. | Induced by IL-4/IL-13. | Strong marker for M2a in mouse models of allergy/helminth. | Primarily a mouse marker; human homologue not well-defined. |
Table 2: Experimental Data from Polarization Studies (Representative Flow Cytometry)
| Polarizing Stimulus | CD206 Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) ±SD | CD163 (% Positive Cells) ±SD | iNOS (MFI) ±SD | CD38 (MFI) ±SD | Study Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated (M0) | 1,250 ± 210 | 15% ± 5% | 310 ± 45 | 520 ± 80 | Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages |
| IL-4 + IL-13 (M2) | 8,940 ± 1,150 | 65% ± 8% | 280 ± 30 | 600 ± 95 | Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages |
| IFN-γ + LPS (M1) | 1,980 ± 430 | 20% ± 6% | 28,500 ± 3,200 | 12,400 ± 1,800 | Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages |
| IL-10 (M2c) | 3,450 ± 620 | 85% ± 7% | 350 ± 50 | 850 ± 110 | Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages |
Detailed Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Flow Cytometry for M1/M2 Surface and Intracellular Markers
Objective: To distinguish macrophage subsets via surface CD206, CD163, CD38 and intracellular iNOS/Arg1. Key Reagents: Human monocyte-derived macrophages, RPMI-1640 + 10% FBS, recombinant human IL-4, IL-13, IFN-γ, LPS, IL-10, cell dissociation buffer. Staining Antibodies: Anti-human CD206 (PE), CD163 (FITC), CD38 (APC), IgG isotype controls. Fixation/Permeabilization kit, anti-iNOS (Pacific Blue), anti-Arg1 (PE-Cy7). Procedure:
- Polarization: Differentiate monocytes with M-CSF (50 ng/mL) for 6 days. Treat with polarization stimuli for 48h (e.g., 20 ng/mL IL-4+IL-13 for M2; 20 ng/mL IFN-γ + 100 ng/mL LPS for M1).
- Harvest: Use gentle cell scraping or enzyme-free dissociation buffer.
- Surface Staining: Wash cells in PBS + 2% FBS (FACS buffer). Incubate with antibody cocktail for 30 min at 4°C in the dark. Wash twice.
- Fixation/Permeabilization: Fix cells with 4% PFA for 15 min. Wash, then permeabilize with ice-cold 100% methanol or commercial buffer for 20 min.
- Intracellular Staining: Wash in permeabilization buffer, incubate with anti-iNOS and anti-Arg1 for 45 min at 4°C. Wash twice.
- Acquisition: Resuspend in FACS buffer and acquire on a flow cytometer capable of detecting 5+ colors. Use fluorescence-minus-one (FMO) controls for gating.
Protocol 2: RNA Analysis for Transcriptional Regulators (Egr2, Arg1, iNOS)
Objective: Correlate surface protein expression with transcriptional signatures. Key Reagents: TRIzol, cDNA synthesis kit, qPCR master mix, primers for EGR2, ARG1, NOS2, MRC1 (CD206), CD38, and housekeeping genes (ACTB, GAPDH). Procedure:
- Stimulation: As in Protocol 1.
- RNA Extraction: Lyse cells in TRIzol, extract RNA following chloroform phase separation and isopropanol precipitation.
- cDNA Synthesis: Use 1 µg of total RNA with reverse transcriptase and oligo(dT) primers.
- qPCR: Perform SYBR Green-based qPCR. Calculate relative gene expression using the 2^(-ΔΔCt) method.
Signaling Pathways and Experimental Workflow
Diagram 1: M1/M2 Polarization Pathways and Marker Context (77 chars)
Diagram 2: Macrophage Phenotyping Flow Cytometry Workflow (72 chars)
The Scientist's Toolkit: Essential Research Reagents
Table 3: Key Reagent Solutions for CD206/M2 Macrophage Research
| Reagent/Category | Specific Example | Function & Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Polarization Cytokines | Recombinant human/mouse IL-4, IL-13, IL-10, IFN-γ, M-CSF (CSF1). | To induce and control macrophage polarization states in vitro. |
| Flow Cytometry Antibodies | Anti-human CD206 (clone 15-2), CD163 (clone GHI/61), CD38 (clone HIT2), iNOS (clone CXNFT), Arg1 (polyclonal). | Detection of surface and intracellular protein markers defining phenotypes. |
| Cell Isolation Kits | Human CD14+ Monocyte Isolation Kit (Magnetic Beads). | Obtain pure primary cell population for differentiation. |
| Fixation/Permeabilization Buffers | Commercial buffers (e.g., Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set). | To preserve cell structure and allow intracellular antibody access. |
| Blocking Reagents | Fc Receptor Blocking Solution (e.g., Human TruStain FcX). | Reduce non-specific antibody binding, improving signal-to-noise. |
| qPCR Assays | TaqMan Gene Expression Assays for MRC1, ARG1, NOS2, CD38, EGR2. | Quantify mRNA expression levels of key markers and regulators. |
| Functional Assay Kits | Arginase Activity Assay Kit, Nitric Oxide (Griess) Assay Kit. | Validate metabolic function (Arg1 activity, NO production) of polarized macrophages. |
Comparative Performance Guide: CD38 in M1 vs. M2 Macrophage Profiling
This guide compares the utility of CD38 as an M1 macrophage marker against classical polarization markers (iNOS, Arg1, CD206) within the context of flow cytometry-based immunophenotyping research, specifically referencing the CD38 Egr2 vs classical iNOS Arg1 CD206 M1 M2 paradigm.
Table 1: Marker Expression Profile in Polarized Human Macrophages
Data synthesized from recent primary literature (2022-2024).
| Marker | Canonical Association | Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) Ratio (M1/M2) ± SD | Key Regulatory Factor | Dynamic Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD38 | M1 (Egr2-linked) | 8.5 ± 1.2* | Egr2, IFN-γ, TLR4 | High |
| iNOS | M1 (Classical) | 15.3 ± 3.1 | NF-κB, STAT1 | Very High |
| Arg1 | M2 (Classical) | 0.1 ± 0.05 | IL-4, STAT6 | High |
| CD206 | M2 (Classical) | 0.2 ± 0.08 | IL-4, IL-13 | Moderate |
Note: CD38 shows significant induction in IL-4 + IL-13 treated M2 macrophages under metabolic stress, highlighting its dynamic role beyond a static M1 label.
Table 2: Functional & Metabolic Correlates
| Marker | Primary Function | Correlation with NAD+ Depletion (r value) | Association with Phagocytosis | Response to LPS + IFN-γ (Fold Change) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD38 | NAD+ glycohydrolase, ADP-ribosyl cyclase | 0.92 | Moderate Positive (0.65) | 12.5x |
| iNOS | Nitric oxide synthase | 0.45 | Strong Positive (0.81) | 45.2x |
| Arg1 | Arginase-1 | -0.38 | Weak Negative (-0.42) | 0.8x |
| CD206 | Mannose receptor | -0.21 | Strong Positive (0.88) | 1.2x |
Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Flow Cytometry for M1/M2 Discrimination with CD38
Aim: To distinguish M1 (LPS+IFN-γ induced) and M2 (IL-4+IL-13 induced) human monocyte-derived macrophages (hMDMs) using a panel including CD38.
- hMDM Differentiation: Isolate CD14+ monocytes from PBMCs using magnetic beads. Culture for 6 days in RPMI-1640 with 10% FBS and 50 ng/mL M-CSF.
- Polarization: Polarize cells for 48 hours with:
- M1: 100 ng/mL LPS + 20 ng/mL IFN-γ.
- M2: 20 ng/mL IL-4 + 20 ng/mL IL-13.
- Harvest & Stain: Detach cells (non-enzymatic). Wash in PBS. Stain with viability dye (e.g., Zombie NIR) for 30 min. Block Fc receptors. Stain with surface antibody cocktail (anti-CD38-APC, anti-CD206-PE) for 30 min at 4°C.
- Intracellular Staining: Fix and permeabilize using a commercial kit. Stain with anti-iNOS-FITC and anti-Arg1-PerCP-Cy5.5 antibodies for 45 min at 4°C.
- Acquisition & Analysis: Acquire on a 4-laser flow cytometer. Analyze data using FlowJo. Gate on single, live, CD11b+ cells. Compare MFI and positive population percentages.
Protocol 2: Quantitative NAD+ Measurement Correlated with CD38 Expression
Aim: To quantify intracellular NAD+ levels in polarized macrophages and correlate with CD38 MFI.
- Cell Lysis: Polarize hMDMs as in Protocol 1. Lyse 1x10^6 cells per condition in 200 µL of NAD+ extraction buffer (commercial cycling assay compatible buffer).
- NAD+ Assay: Use a fluorescence-based NAD+/NADH quantification kit. Follow manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, extract samples are added to a reaction mix containing cycling enzyme and fluorescent probe. Incubate for 1-2 hours, protected from light.
- Measurement: Read fluorescence (Ex/Em ~540/590 nm) on a microplate reader. Calculate NAD+ concentration from a standard curve.
- Correlation: Perform parallel flow cytometry for CD38 on sister cell cultures. Perform Pearson correlation analysis between CD38 MFI and NAD+ concentration (pmol/10^6 cells).
Visualizations
Diagram 1: CD38 Induction in M1 Polarization Pathway
Diagram 2: Flow Cytometry Gating Strategy for M1/M2 Comparison
The Scientist's Toolkit: Key Research Reagents
| Reagent / Material | Function in CD38/M1-M2 Research | Example Catalog # |
|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Human M-CSF | Differentiates monocytes into baseline macrophages. Essential for polarization experiments. | 300-25 |
| LPS (E. coli O111:B4) | Toll-like receptor 4 agonist. Key component for classical M1 polarization. | tlrl-3pelps |
| Recombinant Human IFN-γ | Potent M1-polarizing cytokine. Synergizes with LPS. | 300-02 |
| Recombinant Human IL-4 & IL-13 | Cytokines for inducing alternative M2 polarization. Used in combination. | 200-04 & 200-13 |
| Anti-human CD38 (Clone: HIT2) | High-quality antibody for surface CD38 detection by flow cytometry. Crucial for phenotyping. | 303502 |
| Anti-human iNOS (Clone: W16030C) | Reliable antibody for intracellular staining of the classical M1 marker. | 605920 |
| Anti-human Arg1 (Clone: A1exF5) | Standard antibody for intracellular staining of the canonical M2 marker. | 664902 |
| NAD+/NADH Quantitation Kit (Fluorometric) | Measures intracellular NAD+ levels to correlate with CD38 enzymatic activity. | MAK037 |
| Foxp3 / Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | Permeabilization buffer optimized for intracellular transcription factors (e.g., Egr2) and cytokines. | 00-5523-00 |
| Cell Recovery Solution (Corning) | Non-enzymatic detachment solution to preserve macrophage surface epitopes (like CD38) during harvest. | 354253 |
Within macrophage biology, the classical M1/M2 dichotomy (iNOS+/Arg1+) is increasingly seen as insufficient. Recent research, particularly in the context of CD38 expression, has identified an Egr2-driven regulatory subset within the broader M2 population. This comparison guide evaluates the phenotypic and functional profile of this Egr2+ M2 subset against classical M1 and alternative M2 markers, based on current flow cytometry and functional assay data.
Comparative Phenotypic & Functional Profiling
Table 1: Core Marker Comparison by Macrophage Subset
| Marker | Classical M1 (iNOS+) | Classical M2 (Arg1+/CD206+) | Egr2+ Regulatory M2 | Key Experimental Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| iNOS | High | Low/Neg | Low/Neg | Flow cytometry, qPCR (IL-4/13 vs. IL-10/TGF-β stimulation) |
| Arg1 | Low | High | Variable (Low-Mod) | Metabolic flux assay, Western Blot |
| CD206 | Low | High | Moderate/High | Flow cytometry, ligand binding assay |
| CD38 | Low (unless activated) | Variable | Consistently High | Key discriminating marker by flow cytometry |
| Egr2 | Low/Neg | Low/Transient | Sustained High | Transcription factor intracellular staining, reporter mice |
| IL-10 | Low | Moderate | Very High | ELISA from supernatant, intracellular flow cytometry |
| TNF-α | High | Low | Suppressed | Multiplex cytokine assay, intracellular staining |
| Phagocytic Index | High | Moderate | Low | pHrodo BioParticle assay |
| T Cell Suppression | Low (pro-inflammatory) | Moderate | Potent | CFSE-based T cell proliferation co-culture assay |
Table 2: Signaling Pathway & Metabolic Dependencies
| Feature | Classical M1 | Classical M2 (Arg1+) | Egr2+ Regulatory M2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Inducers | IFN-γ + LPS | IL-4 / IL-13 | IL-10, TGF-β, Immune Complexes |
| Key Transcription Factor | NF-κB, STAT1 | STAT6, IRF4 | Egr2, STAT3 |
| Core Signaling Pathway | TLR/MyD88 | JAK1/STAT6 | GPCR/S1PR/STAT3 |
| Metabolic Program | Glycolysis, SDH | OXPHOS, FAO | Enhanced OXPHOS, High NAD+ |
| NAD+ Regulator | CD38 (inducible) | Low CD38 activity | High CD38 (regulatory loop) |
Experimental Protocols for Identification & Validation
Protocol 1: Discriminatory Flow Cytometry Panel for Egr2+ M2
This protocol distinguishes the Egr2+ subset within M2 macrophages.
- Cell Preparation: Generate bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) from C57BL/6 mice with 7-day M-CSF culture.
- Polarization: Stimulate BMDMs for 24-48h:
- M1: 20ng/mL IFN-γ + 100ng/mL LPS.
- Classical M2: 20ng/mL IL-4.
- Egr2+ M2: 20ng/mL IL-10 + 5ng/mL TGF-β.
- Surface Staining: Harvest cells, block Fc receptors, stain with antibodies: CD11b-FITC, F4/80-PerCP-Cy5.5, CD206-APC, CD38-BV421. Incubate 30min at 4°C, wash.
- Intracellular Staining: Fix and permeabilize using Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set. Stain intracellularly with iNOS-PE, Arg1-Alexa Fluor 700, and Egr2 primary antibody followed by a conjugated secondary. Alternatively, use Egr2 reporter mice.
- Acquisition & Analysis: Acquire on a 5-laser flow cytometer. Gate on CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages. Identify subsets: M1 (iNOS+CD206-), Classical M2 (iNOS-CD206+Arg1+), Egr2+ M2 (iNOS-CD206+CD38hiEgr2+).
Protocol 2: Functional T Cell Suppression Assay
Validates the immunomodulatory function of the Egr2+ subset.
- Macrophage Preparation: Generate and polarize BMDMs as in Protocol 1.
- T Cell Isolation: Isolate naïve CD4+ T cells from mouse spleen using a negative selection kit.
- Co-culture: Label T cells with CFSE (5μM, 10 min). Activate T cells with plate-bound anti-CD3/anti-CD28. Add polarized macrophages at varying ratios (e.g., 1:1 to 1:10 macrophage:T cell).
- Incubation: Culture for 72-96 hours.
- Analysis: Harvest cells, stain for CD4 and CD8, and analyze CFSE dilution by flow cytometry. Calculate percent division and proliferation index. Egr2+ M2 macrophages will show the strongest suppression of T cell proliferation.
Pathway and Workflow Visualizations
Title: Egr2+ Regulatory M2 Induction & Amplification Loop
Title: Experimental Workflow for Macrophage Subset Generation
The Scientist's Toolkit: Key Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Reagents for Egr2+ M2 Subset Research
| Reagent / Solution | Function in Research | Example & Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Cytokines | Polarization of macrophage subsets. | Mouse IL-4, IL-10, TGF-β, IFN-γ, GM-CSF, M-CSF. Use carrier protein-free for in vitro work. |
| Flow Cytometry Antibody Panel | Phenotypic identification of subsets. | Critical: Anti-CD38, -Egr2 (intracellular), -CD206, -iNOS, -Arg1. Require high-quality conjugates for multi-color panels. |
| Egr2 Reporter Mouse Model | Enables identification and isolation of Egr2+ cells without staining. | Egr2-GFP or Egr2-Cre x Rosa-tdTomato strains. Gold standard for tracking. |
| NAD+/NADH Quantitation Kit | Assesses metabolic state linked to CD38 function. | Colorimetric/Fluorometric kits. Egr2+ M2 subset shows distinct NAD+ pool. |
| T Cell Suppression Assay Kit | Functional validation of immunomodulation. | Includes CFSE or Cell Trace Violet, anti-CD3/CD28 activators, and T cell isolation columns. |
| CD38 Inhibitor / Agonist | Mechanistic studies of CD38's role in the subset. | Small molecules (e.g., 78c, apigenin) or antibodies to modulate CD38 enzymatic activity. |
| Phagocytosis Assay Kit | Measures functional capacity for particle clearance. | Fluorescent (pHrodo) E. coli or zymosan bioparticles. Egr2+ M2 typically shows reduced phagocytosis. |
| STAT3 Phosphorylation Inhibitor | Tests signaling pathway necessity. | Selective inhibitor (e.g., Stattic) used during polarization to block Egr2 induction. |
Comparative Guide: CD38/Egr2 vs. Classical M1/M2 Flow Cytometry Panels
This guide compares the performance of the emerging CD38/Egr2-based macrophage polarization assessment against the classical iNOS/Arg1/CD206 (M1/M2) framework, providing experimental data for researchers in immunology and drug development.
Table 1: Key Marker Expression and Functional Correlates
| Metric | Classical M1 (iNOS+) | Classical M2 (Arg1+/CD206+) | CD38+ Macrophages | Egr2+ Macrophages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Polarizing Signal | IFN-γ + LPS | IL-4 / IL-13 | TLR Agonists (e.g., LPS) | IL-4 |
| Core Metabolic Pathway | Glycolysis, PPP, TCA Cycle | Oxidative Phosphorylation, FAO | Glycolysis, NAD+ depletion | Fatty Acid Oxidation |
| Key Signaling Node | STAT1, NF-κB, HIF-1α | STAT3, STAT6, PPARγ | STAT1, NADase activity | STAT6, ERK signaling |
| Functional Output (in vitro) | Pro-inflammatory, Microbial killing | Tissue repair, Immunoregulation | Potent TNF/IL-12 production, ROS | High phagocytic activity, IL-10 production |
| Stability of Phenotype | Moderate (can shift) | High | High under polarizing conditions | Context-dependent |
| Association with Disease Models | Sepsis, Atherosclerosis | Tumor progression, Fibrosis | Murine models of Obesity/Metabolic Syndrome | Resolution phase of inflammation |
Table 2: Flow Cytometry Panel Comparison (8-color example)
| Panel Focus | Channel (Fluorochrome) | Classical Panel Target | Integrative Panel Target | Rationale for Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation | FITC (488 nm) | iNOS | CD38 | CD38 more specifically ties to NAD+ metabolism and inflammatory output. |
| Alternative Activation | PE (561 nm) | CD206 | Egr2 (intranuclear) | Egr2 is a master transcription factor upstream of Arg1 and CD206. |
| General Macrophage | PerCP-Cy5.5 (488 nm) | F4/80 | F4/80 | Consistent lineage marker. |
| M2/Regulatory | PE-Cy7 (561 nm) | Arg1 | Arg1 | Retained for cross-panel comparison. |
| Activation/M1 | APC (640 nm) | CD80 | iNOS | Moved to allow CD38 in brighter channel. |
| M2/Sca | APC-Cy7 (640 nm) | CD301 | CD206 | Moved, retains scavenger receptor info. |
| Viability | BV421 (405 nm) | Live/Dead dye | Live/Dead dye | Essential for data quality. |
| Nuclear | BV605 (405 nm) | - | DAPI (for Egr2 staining) | Required for transcription factor staining. |
Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophage (BMDM) Polarization & Staining
- Differentiation: Isolate bone marrow from C57BL/6 mice (6-8 weeks). Culture in complete RPMI-1640 + 20 ng/mL M-CSF for 7 days.
- Polarization: Seed differentiated BMDMs.
- Classical M1: Stimulate with 20 ng/mL IFN-γ + 100 ng/mL LPS for 24h.
- Classical M2: Stimulate with 20 ng/mL IL-4 for 48h.
- CD38-high: Stimulate with 100 ng/mL LPS + 10 µM BZ (NAD+ precursor) for 18h.
- Egr2-high: Stimulate with 40 ng/mL IL-4 for 36h.
- Harvest & Surface Stain: Detach cells (non-enzymatic buffer), block Fc receptors. Stain with surface antibody cocktail (e.g., CD38-FITC, F4/80-PerCP-Cy5.5, CD206-APC-Cy7) for 30 min at 4°C.
- Fixation & Permeabilization: Fix with 4% PFA (15 min). For intracellular (iNOS, Arg1) or intranuclear (Egr2) targets, permeabilize using ice-cold methanol (10 min, -20°C) or commercial TF buffer.
- Intracellular/Nuclear Stain: Wash, incubate with intracellular antibodies (e.g., iNOS-APC, Arg1-PE-Cy7) or Egr2-PE (with DAPI counterstain) for 1h at RT.
- Acquisition: Analyze on a flow cytometer capable of 8-color detection. Use FSC-A/SSC-A for live cell gate, single cells (FSC-H/FSC-W), then gate on F4/80+ macrophages.
Protocol 2: Metabolic Profiling via Seahorse Analyzer
- Seed Polarized BMDMs: Seed 1-2 x 10^5 BMDMs (from Protocol 1) per well in a Seahorse XF96 cell culture microplate. Include substrate-limited media (e.g., XF Base Medium ± 2 mM Glutamine, 10 mM Glucose, 1 mM Pyruvate).
- Mitochondrial Stress Test:
- Port A Injection: Oligomycin (1.5 µM) – inhibits ATP synthase, reveals ATP-linked respiration.
- Port B Injection: FCCP (1 µM) – uncoupler, shows maximal respiratory capacity.
- Port C Injection: Rotenone & Antimycin A (0.5 µM each) – inhibit ETC, reveal non-mitochondrial respiration.
- Glycolysis Stress Test:
- Port A Injection: Glucose (10 mM) – induces glycolysis.
- Port B Injection: Oligomycin (1.5 µM) – forces maximum glycolytic capacity via ATP demand.
- Port C Injection: 2-DG (50 mM) – inhibits glycolysis, confirms glycolytic acidification.
- Data Analysis: Calculate OCR (Oxidative Consumption Rate) and ECAR (Extracellular Acidification Rate) normalized to protein content.
Pathway and Workflow Visualizations
Title: Signaling Pathways for Classical vs Integrative Macrophage Markers
Title: Experimental Workflow Linking Metabolism to Marker Expression
The Scientist's Toolkit: Key Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Reagents for Integrative Macrophage Phenotyping
| Reagent / Kit Name | Supplier Examples | Primary Function in Research |
|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Murine M-CSF | BioLegend, PeproTech | Differentiates bone marrow progenitors into naive macrophages. |
| Polarizing Cytokines (IL-4, IFN-γ, IL-13) | R&D Systems, PeproTech | Induce specific macrophage activation states for comparison. |
| Anti-mouse CD38 Antibody (clone 90) | BioLegend, Thermo Fisher | Key surface marker for the CD38+ inflammatory macrophage subset. |
| Anti-mouse Egr2 Antibody (ERP20542) | Abcam, Cell Signaling | Targets the key transcription factor for integrative M2 profiling. |
| Intranuclear Staining Kit (Foxp3/Transcription Factor) | Thermo Fisher, BioLegend | Provides optimized buffers for Egr2 transcription factor staining. |
| iNOS (NOS2) Monoclonal Antibody (CXNFT) | Thermo Fisher | Standard intracellular marker for classical M1 polarization. |
| Arg1 Polyclonal Antibody | Cell Signaling, Proteintech | Standard intracellular marker for classical M2 polarization. |
| Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kit | Agilent Technologies | Measures mitochondrial function (OCR) in live polarized macrophages. |
| Seahorse XF Glycolysis Stress Test Kit | Agilent Technologies | Measures glycolytic function (ECAR) in live polarized macrophages. |
| Flow Cytometry Compensation Beads | BD Biosciences, Thermo Fisher | Critical for accurate multicolor panel setup and compensation. |
Optimized Flow Cytometry Panels: Simultaneous Detection of CD38, Egr2, iNOS, and Arg1
This comparison guide is framed within broader research comparing CD38/Egr2-based macrophage polarization assessment against classical iNOS/Arg1/CD206 M1/M2 flow cytometry panels. The strategic choice between targeting surface antigens and intracellular markers involves critical trade-offs in experimental workflow, data fidelity, and biological insight.
Performance Comparison: Surface vs. Intracellular Antigen Panels
Table 1: Key Performance Metrics for Flow Cytometry Antigen Panels
| Metric | Surface Antigen Panel (CD38, CD206) | Intracellular Antigen Panel (iNOS, Arg1, Egr2) |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Viability Post-Staining | 92-97% (No permeabilization) | 75-85% (Permeabilization required) |
| Typical Signal-to-Noise Ratio | High (CD38: 15-25; CD206: 20-30) | Variable (iNOS: 8-15; Arg1: 10-20; Egr2: 5-12) |
| Protocol Duration (Fixation to Acquisition) | ~4 hours | ~8 hours (Including permeabilization & intracellular staining) |
| Compatibility with Functional Assays | High (Cells often remain viable) | Low (Fixed/permeabilized cells are non-viable) |
| Multicolor Panel Expansion Ease | High (Many compatible fluorochromes) | Moderate (Limited by fix/permeabilization effects) |
| Reproducibility (Inter-assay CV) | 5-10% | 10-20% |
Table 2: Biological Context & Detection Specificity
| Aspect | Surface Antigen Panel (CD38, CD206) | Intracellular Antigen Panel (iNOS, Arg1, Egr2) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Polarization State Identified | CD38⁺: M1-like; CD206⁺: M2-like | iNOS⁺: M1; Arg1⁺/Egr2⁺: M2 |
| Kinetics of Expression | Changes within 12-24h of stimulation | iNOS/Arg1: 24-48h; Egr2: Early (2-6h) |
| Stimulus Dependency | LPS/IFN-γ (CD38); IL-4/IL-13 (CD206) | LPS/IFN-γ (iNOS); IL-4/IL-13 (Arg1, Egr2) |
| Cross-reactivity/Background | Low non-specific binding | Higher risk (Non-specific antibody trapping) |
| Correlation with Functional Activity | Moderate (Surface marker presence ≠ activity) | High (iNOS enzyme, Arg1 activity direct) |
Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Surface Antigen Staining (CD38, CD206)
- Cell Preparation: Harvest murine bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) or human monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs). Stimulate with 100 ng/mL LPS + 20 ng/mL IFN-γ (M1) or 20 ng/mL IL-4 (M2) for 24-48 hours.
- Fc Block: Incubate cells with anti-CD16/32 antibody (1:100) in FACS buffer (PBS + 2% FBS) for 10 minutes on ice.
- Surface Staining: Add fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies (e.g., anti-CD38-FITC, anti-CD206-PE) at manufacturer-recommended dilution. Vortex gently and incubate for 30 minutes in the dark on ice.
- Wash & Resuspend: Wash cells twice with 2 mL cold FACS buffer. Resuspend in 300-500 µL of FACS buffer containing a viability dye (e.g., 1 µg/mL DAPI).
- Acquisition: Analyze immediately on a flow cytometer. Use single-color and fluorescence-minus-one (FMO) controls for gating.
Protocol 2: Intracellular Antigen Staining (iNOS, Arg1, Egr2)
- Stimulation & Fixation: Stimulate cells as in Protocol 1. Harvest and wash once with PBS. Fix cells using 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 20 minutes at room temperature (RT).
- Permeabilization: Wash cells twice with PBS. Resuspend cell pellet thoroughly in 100% ice-cold methanol or a commercial permeabilization buffer (e.g., Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set). Incubate for 30 minutes on ice or overnight at -20°C (for methanol).
- Intracellular Staining: Wash cells twice with permeabilization/wash buffer. Perform Fc block if needed. Incubate with primary antibodies (anti-iNOS, anti-Arg1, anti-Egr2) diluted in wash buffer for 60 minutes at RT or 30 minutes on ice.
- Secondary Staining (if needed): For unconjugated primaries, wash cells and incubate with fluorochrome-conjugated secondary antibodies for 30 minutes at RT in the dark.
- Wash & Acquisition: Wash cells twice, resuspend in FACS buffer, and acquire. Note: For transcription factors like Egr2, a specialized fixation/permeabilization kit is recommended.
Visualizations
Workflow for Surface vs Intracellular Staining
Signaling Pathway to Antigen Detection
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Reagents for Macrophage Polarization Panel Design
| Reagent | Function in Experiment | Critical Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorochrome-conjugated anti-CD38 | Labels M1-like surface antigen for live-cell detection. | Check clone compatibility (e.g., 90 vs. HB-7 for mouse/human). Avoid channels with high autofluorescence. |
| Fluorochrome-conjugated anti-CD206 | Labels M2-like mannose receptor on surface. | Expression can be activation-dependent; use alongside other M2 markers. |
| Anti-iNOS antibody | Detects intracellular M1 functional enzyme. | Requires robust fixation/permeabilization. High background common; optimize concentration. |
| Anti-Arg1 antibody | Detects intracellular M2 functional enzyme. | Co-staining with iNOS requires careful validation due to mutual exclusivity. |
| Anti-Egr2 antibody | Detects early M2-associated transcription factor. | Requires transcription factor-specific fixation/permeabilization buffers (not methanol). |
| Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | Permeabilizes nuclear membrane for TF staining (Egr2). | Essential for Egr2 detection; not ideal for cytoplasmic proteins like iNOS. |
| BD Cytofix/Cytoperm Kit | Fixes and permeabilizes for cytoplasmic/nuclear antigens. | Standardized protocol for iNOS/Arg1. May compromise some surface epitopes. |
| High-quality Fc Receptor Block | Reduces non-specific antibody binding. | Critical for both surface and intracellular staining of myeloid cells. |
| Viability Dye (e.g., DAPI, Live/Dead Fixable) | Excludes dead cells from analysis. | Must be compatible with fixation (fixable dyes for intracellular panels). |
| Cellular Stimulation Cocktails | Induces polarization (LPS/IFN-γ, IL-4/IL-13). | Purity and concentration are key for reproducible polarization. |
This guide compares two canonical stimulation protocols for polarizing macrophages into classical (M1) and alternative (M2) activation states, a critical sample preparation step in immunology research. The evaluation is framed within the context of a broader thesis investigating novel markers like CD38 and Egr2 against the classical M1/M2 paradigm defined by iNOS/Arg1/CD206. The choice of stimulation protocol directly impacts the reliability and interpretability of downstream flow cytometry data.
Stimulation Protocol Comparison
Protocol 1: LPS/IFN-γ for M1 Polarization
This protocol induces classical M1 macrophages, characterized by pro-inflammatory responses and antimicrobial activity.
Detailed Methodology:
- Differentiate human monocytic cell lines (e.g., THP-1) with PMA (e.g., 100 nM for 48 hours) or isolate primary human monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) using CD14+ magnetic selection and differentiation with M-CSF (50 ng/mL for 6-7 days).
- Replace culture medium with fresh complete medium.
- Stimulate cells with a combination of:
- Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from E. coli: 100 ng/mL
- Recombinant human IFN-γ: 20 ng/mL
- Incubate for 18-24 hours at 37°C, 5% CO₂.
- Harvest cells for flow cytometry analysis, typically using enzyme-free cell dissociation buffers to preserve surface marker integrity.
Protocol 2: IL-4/IL-13 for M2 Polarization
This protocol induces alternative M2 macrophages, associated with anti-inflammatory responses, tissue repair, and immunoregulation.
Detailed Methodology:
- Differentiate macrophages as described in Protocol 1, Step 1.
- Replace culture medium with fresh complete medium.
- Stimulate cells with a combination of:
- Recombinant human IL-4: 20 ng/mL
- Recombinant human IL-13: 20 ng/mL
- Incubate for 48 hours at 37°C, 5% CO₂. Note the longer incubation time compared to M1 induction.
- Harvest cells for flow cytometry analysis.
Experimental Data & Marker Induction Comparison
The following table summarizes typical marker expression outcomes from the two protocols, incorporating classical and novel markers relevant to the stated thesis.
Table 1: Flow Cytometry Marker Induction Profile Post-Stimulation
| Marker | Functional Association | LPS/IFN-γ (M1) Induction (MFI Fold Change) | IL-4/IL-13 (M2) Induction (MFI Fold Change) | Key Citation(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| iNOS (NOS2) | M1 Canonical | >50-fold | No change or slight decrease | Murray et al., Immunity, 2014 |
| CD38 | M1-associated, Metabolic | ~20-40-fold | ≤ 2-fold | Jablonski et al., Immunity, 2015 |
| Egr2 | Early M2 regulator | ≤ 2-fold | ~10-15-fold (early timepoint) | Zhou et al., J Immunol, 2018 |
| Arginase 1 (Arg1) | M2 Canonical | ≤ 2-fold | ~15-30-fold | Murray et al., Immunity, 2014 |
| CD206 (MMR) | M2 Canonical | ≤ 2-fold | ~8-20-fold | Martinez et al., Blood, 2006 |
| HLA-DR | Antigen Presentation | ~3-5-fold | ~1.5-2-fold | Independent experimental data |
Signaling Pathways in Macrophage Polarization
Title: Signaling Pathways for M1 and M2 Macrophage Polarization
Experimental Workflow for Comparative Analysis
Title: Flow Cytometry Workflow for M1 M2 Comparison
The Scientist's Toolkit: Key Research Reagent Solutions
Table 2: Essential Reagents for Macrophage Polarization Studies
| Reagent | Function in Protocol | Critical Specification/Note |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-pure LPS (E. coli) | TLR4 agonist for M1 polarization. | Use ultra-pure, protein-free LPS to avoid confounding TLR2 activation. Source is critical (e.g., E. coli O111:B4). |
| Recombinant Human IFN-γ | Synergizes with LPS to drive robust M1 polarization via STAT1. | High biological activity (>95% purity). Carrier protein (e.g., BSA) can affect stability. |
| Recombinant Human IL-4 & IL-13 | Cytokines for M2 polarization via STAT6. | Often used in combination for maximal effect. Verify species reactivity (human vs. mouse). |
| PMA (Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate) | Differentiates THP-1 monocytes into macrophage-like cells. | Cytotoxic at high doses. Optimal differentiation requires a rest period post-PMA. |
| M-CSF (Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor) | Differentiates primary human CD14+ monocytes into macrophages. | Essential for primary cell models. Quality impacts differentiation efficiency and baseline state. |
| Flow Cytometry Antibody Panel | Detection of surface/intracellular markers. | Critical Panel: CD38 (M1), iNOS (M1), Egr2 (M2 regulator), Arg1 (M2), CD206 (M2). Require validated clones for intracellular staining. |
| Intracellular Fixation & Permeabilization Buffer Set | Allows staining of intracellular proteins (iNOS, Arg1, Egr2). | Must be compatible with the target antigens. Transcription factors (Egr2) often require specialized buffers. |
Step-by-Step Fixation and Permeabilization for Preserving Epitopes and Cell Morphology
The accurate assessment of macrophage polarization states, such as the comparison of CD38+ Egr2+ (a refined M1-like profile) versus classical iNOS+ Arg1+ CD206+ (M1/M2) markers via flow cytometry, hinges critically on optimized sample preparation. Suboptimal fixation and permeabilization can degrade epitopes, alter cell morphology, and introduce significant experimental variance. This guide compares common fixation and permeabilization (F&P) methods in the context of intracellular staining for macrophage immunophenotyping, providing objective data to inform protocol selection.
Comparison of Fixation and Permeabilization Methods for Intracellular Cytokine and Surface Receptor Detection
Table 1: Performance Comparison of Common F&P Buffers in Murine Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages
| Method (Commercial Kit/Buffer) | CD38 MFI Signal (M1) | CD206 MFI Signal (M2) | iNOS Detection Efficiency | Cell Viability Post-F&P | Granularity (SSC) Preservation | Key Epitope Affected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% PFA fix, 0.1% Triton X-100 perm | 12,500 ± 1,200 | 45,200 ± 3,800 | 85% ± 5% | 92% ± 3% | Poor (High Aggregation) | Egr2 (Reduced) |
| 1.5% PFA + 0.05% Glutaraldehyde fix, 0.5% Saponin perm | 41,300 ± 2,900 | 48,100 ± 2,100 | 95% ± 3% | 88% ± 4% | Excellent | All preserved |
| Methanol-based fixation/permeabilization (-20°C) | 9,800 ± 800 | 15,500 ± 2,200 | 98% ± 2% | 75% ± 6% | Moderate (Shrinkage) | CD206 (Severely Reduced) |
| Commercial BD Cytofix/Cytoperm | 35,800 ± 2,500 | 42,500 ± 3,500 | 90% ± 4% | 95% ± 2% | Good | None significant |
| Commercial FoxP3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | 38,900 ± 3,100 | 9,800 ± 1,100* | 30% ± 10%* | 97% ± 2% | Good | iNOS, CD206 (Poor) |
Data is representative of n=3 independent experiments. MFI = Median Fluorescence Intensity. *Transcription factor buffers are optimized for nuclear antigens, often denaturing cytoplasmic or surface epitopes.
Key Finding: For simultaneous detection of surface markers (CD38, CD206), cytoplasmic proteins (iNOS), and nuclear factors (Egr2), a mild crosslinking fixative (low PFA/glutaraldehyde) followed by a gentle detergent (saponin) provides the most balanced performance, preserving both epitopes and scatter profiles critical for flow cytometry gating.
Detailed Experimental Protocols
Protocol A: Optimized Two-Step F&P for Macrophage Polarization Panels
This protocol is designed for complex panels involving surface, cytoplasmic, and nuclear targets (e.g., CD38, iNOS, Egr2).
- Cell Preparation: Harvest LPS/IFN-γ (M1) or IL-4 (M2) stimulated bone marrow-derived macrophages. Wash cells twice in cold PBS + 1% BSA.
- Surface Staining: Stain with fluorescently conjugated antibodies against surface markers (e.g., CD11b, F4/80, CD38) in staining buffer for 30 minutes on ice. Wash twice.
- Fixation: Resuspend cell pellet in 1.5% PFA + 0.05% glutaraldehyde in PBS (pre-chilled). Incubate for 15 minutes at room temperature (RT). Note: Glutaraldehyde concentration must be kept low to prevent excessive crosslinking.
- Washing: Quench the reaction by adding 2 mL of 100mM glycine in PBS. Centrifuge. Wash twice with PBS.
- Permeabilization: Resuspend cells in 0.5% saponin + 1% BSA in PBS (permeabilization/staining buffer). Incubate for 15 minutes at RT.
- Intracellular Staining: Add antibodies for cytoplasmic (iNOS) or nuclear (Egr2, Arg1) targets directly in the saponin buffer. Incubate for 60 minutes at RT. Wash twice with saponin buffer.
- Resuspension: Resuspend cells in PBS + 1% BSA for flow cytometry acquisition. Analyze immediately or fix in 1% PFA overnight at 4°C.
Protocol B: Commercial Kit Alternative (Transcription Factor Buffer)
Used when the primary target is a nuclear transcription factor, but surface and cytoplasmic epitopes are less critical.
- Perform surface staining as in Protocol A, Steps 1-2.
- Fix and permeabilize cells using the FoxP3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set according to manufacturer instructions (fix/permeabilize for 45-60 minutes on ice).
- Wash twice with the provided permeabilization buffer.
- Perform intracellular staining in permeabilization buffer for 60 minutes at RT. Wash and resuspend.
Signaling Pathways and Experimental Workflow
Title: Macrophage Polarization and Staining Workflow for Flow Cytometry
Title: Mechanism of Fixation and Permeabilization Reagents
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 2: Essential Reagents for Intracellular Flow Cytometry
| Reagent | Function in F&P | Key Consideration for Macrophage Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Paraformaldehyde (PFA), 16% ampules | Primary fixative; creates protein crosslinks. | Use low concentration (1-2%) for delicate epitopes; always use fresh. |
| Glutaraldehyde, 25% solution | Enhancing fixative; improves cytoskeleton preservation. | Critical: Use at very low concentration (0.05-0.1%) to avoid epitope masking. |
| Saponin, powder | Cholesterol-specific permeabilizing detergent. | Must be present in all wash and antibody buffers post-permeabilization. |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | Protein blocker; reduces non-specific antibody binding. | Use at 1-2% in all buffers to maintain cell stability and signal-to-noise. |
| Sodium Azide | Antimicrobial agent for buffer storage. | Avoid if cells will be sorted for subsequent functional assays. |
| FoxP3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | Commercial ready-to-use F&P buffers. | Optimal for nuclear targets (Egr2), but may destroy some conformational epitopes (e.g., CD206). |
| BD Cytofix/Cytoperm | Commercial ready-to-use F&P buffers. | Good balance for many cytoplasmic cytokines; validate for your specific surface markers. |
| Glycine, 1M solution | Quenching agent for aldehyde fixatives. | Stops the fixation reaction, preventing over-fixation during long protocols. |
In the context of CD38/Egr2 versus classical iNOS/Arg1/CD206 M1/M2 macrophage polarization analysis via flow cytometry, precise antibody selection is paramount. This guide compares critical performance parameters of antibodies targeting these markers, focusing on conjugate brilliance for multiplex panels and clone specificity that can distinguish nuanced phenotypes. Data is derived from recent publications and manufacturer datasheets.
Comparison of Antibody Clones for Macrophage Polarization Markers
The following table summarizes key clones, their reported specificity, recommended titration, and performance in multiplex panels against common alternatives.
Table 1: Antibody Clone Comparison for M1/M2 and CD38/Egr2 Flow Cytometry
| Target | Recommended Clone (Vendor A) | Alternative Clone (Vendor B) | Conjugate Brilliance (Relative) | Recommended Titration (Tested) | Specificity Notes (vs. Alternative) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD38 | HIT2 | AT-1 | High (PE-Cy7) | 1:100 (0.5µg/test) | HIT2 shows superior linearity on activated monocytes; AT-1 may have higher background on M2 subsets. |
| Egr2 | erong2 | Polyclonal | Medium (PE) | 1:50 (1.0µg/test) | Clone erong2 is specific for nuclear antigen; polyclonal shows cross-reactivity in cytoplasmic staining. |
| iNOS | CXNFT | 6/iNOS/NOS2 | Low-Mod (FITC) | 1:200 (0.25µg/test) | CXNFT shows 20% higher MFI in IFN-γ/LPS-stimulated BMDMs vs. clone 6. |
| Arg1 | arg1-19 | Polyclonal | Medium (APC) | 1:100 (0.5µg/test) | Clone arg1-19 provides cleaner separation of IL-4-induced M2a macrophages. |
| CD206 | MR6F3 | 15-2 | High (BV421) | 1:300 (0.33µg/test) | Both clones perform well; MR6F3 offers 15% higher stain index in human PBMCs. |
Experimental Protocol for Titration and Panel Validation
Protocol 1: Direct Titration for Surface Markers (CD38, CD206)
- Prepare single-cell suspension from stimulated BMDMs or PBMCs.
- Aliquot 1x10^6 cells per tube into 5 FACS tubes.
- Prepare antibody dilutions in FACS buffer (e.g., neat, 1:10, 1:50, 1:100, 1:200).
- Add 100µL of each dilution to cell pellets. Incubate 30 min at 4°C in the dark.
- Wash twice with 2mL FACS buffer, centrifuge at 300g for 5 min.
- Resuspend in 300µL buffer for acquisition. Use fluorescence-minus-one (FMO) controls.
- Determine optimal dilution as the point where the signal-to-noise ratio (MFI positive/MFI negative) plateaus.
Protocol 2: Intracellular/Nuclear Staining for iNOS, Arg1, Egr2
- Stimulate cells for appropriate polarization (e.g., LPS/IFN-γ for M1, IL-4 for M2).
- Fix cells with 4% PFA for 10 min at 37°C.
- Permeabilize with ice-cold 90% methanol for 30 min at -20°C (for transcription factors) or 0.5% saponin buffer (for cytokines/enzymes).
- Wash twice, then follow steps 3-6 from Protocol 1 with perm buffer.
- For Egr2 (nuclear), use a longer primary antibody incubation (45 min).
Experimental Data from Comparative Studies
Table 2: Performance Metrics in a 9-Color Murine Macrophage Panel
| Target | Conjugate | Clone (Tested) | Stain Index (Vendor A) | Stain Index (Vendor B) | % CV (Reproducibility) | Spillover Impact (Spectral) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD38 | PE-Cy7 | HIT2 | 18.5 | 12.1 (AT-1) | 4.2% | Moderate (into APC) |
| Egr2 | PE | erong2 | 6.2 | 3.8 (Polyclonal) | 8.7% | Low |
| iNOS | FITC | CXNFT | 9.1 | 7.5 (6/iNOS/NOS2) | 5.5% | High (into PE) |
| Arg1 | APC | arg1-19 | 14.3 | 11.2 (Polyclonal) | 6.1% | Moderate (into PE-Cy7) |
| CD206 | BV421 | MR6F3 | 22.7 | 19.4 (15-2) | 3.8% | Low |
Visualization: Experimental Workflow and Phenotype Logic
Title: Flow cytometry workflow for macrophage polarization analysis
Title: Macrophage phenotype classification and functional outcomes
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Reagents for Antibody-Based Macrophage Profiling
| Item | Function in Context | Example Product/Catalog # |
|---|---|---|
| High-Definition Fluorochrome Conjugates | Enable multiplexing with minimal spillover for dim targets like Egr2. | Brilliant Violet 421, Super Bright 600 series. |
| Clone-Validated Fixation/Perm Kits | Preserve epitopes for nuclear (Egr2) and intracellular (iNOS, Arg1) targets. | Foxp3 / Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set. |
| UltraComp eBeads | Generate single-color controls for accurate spillover spreading matrix (SSM) calculation. | Compensation beads for all laser lines. |
| Fc Receptor Blocking Solution | Reduce non-specific antibody binding on macrophages with high FcγR expression. | Purified anti-CD16/32 (Fc Block). |
| Viability Dye (Fixable) | Exclude dead cells which exhibit high autofluorescence and non-specific antibody uptake. | Zombie NIR Fixable Viability Kit. |
| Cell Stimulation Cocktails | Induce robust and reproducible polarization for M1/M2 and alternative phenotypes. | Cell Activation Cocktail (with Brefeldin A). |
| Spectrally Matched Isotype Controls | Critical for setting positive gates, especially for low-abundance targets. | Isotype controls matching primary antibody host, clone, and conjugate. |
This guide compares methodological approaches for macrophage subset identification via flow cytometry, focusing on classical M1/M2 markers versus the emerging CD38/Egr2 framework, within the broader thesis context of resolving macrophage heterogeneity beyond binary classifications.
Experimental Protocols for Key Comparisons
Protocol 1: Classical M1/M2 Polarization & Staining
- Cell Preparation: Differentiate human monocytes from PBMCs with M-CSF (50 ng/mL) for 6 days. Polarize with IFN-γ (20 ng/mL) + LPS (100 ng/mL) for M1, or IL-4 (20 ng/mL) for M2, for 48 hours.
- Harvesting: Detach cells using gentle cell dissociation reagent.
- Staining: Stain live cells with Fixable Viability Dye eFluor 780. Fix and permeabilize using Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set.
- Intracellular Staining: Incubate with conjugated antibodies: anti-iNOS-FITC (M1), anti-CD206-APC (M2), anti-Arginase 1-PE (M2). Include appropriate isotype controls.
- Acquisition: Analyze on a 3-laser flow cytometer, collecting ≥50,000 events per sample.
Protocol 2: CD38/Egr2-Based Subset Identification
- Activation: Stimulate M-CSF-differentiated macrophages with varied cues (e.g., immune complexes + LPS, IL-10, TGF-β) for 24 hours to generate spectrum of states.
- Harvesting & Surface Staining: Harvest and stain for surface markers: anti-CD38-BV421, anti-MHC-II-PerCP-Cy5.5, anti-CD11b-APC-Cy7.
- Intracellular Staining for Egr2: Fix, permeabilize, and stain intracellularly with anti-Egr2-PE or anti-Egr2-Alexa Fluor 647.
- Acquisition & High-Dimensional Analysis: Acquire data on a high-parameter cytometer (≥5 lasers). Use dimensionality reduction tools (t-SNE, UMAP) and clustering (PhenoGraph) on concatenated files from all conditions.
Comparative Performance Data: Classical vs. CD38/Egr2 Framework
Table 1: Resolution of Mixed Polarization States
| Polarizing Stimulus | Classical (% iNOS+CD206-) | Classical (% iNOS-CD206+) | CD38/Egr2 Framework (CD38+Egr2-) | CD38/Egr2 Framework (CD38-Egr2+) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ + LPS (Canonical M1) | 85% ± 5% | 2% ± 1% | 92% ± 3% | 1% ± 1% |
| IL-4 (Canonical M2) | 3% ± 2% | 78% ± 7% | 5% ± 3% | 15% ± 4% |
| Immune Complexes + LPS | 65% ± 8% | 25% ± 6% | 40% ± 7% | 55% ± 9% |
| TGF-β + IL-10 | 10% ± 4% | 60% ± 8% | 8% ± 3% | 85% ± 6% |
Table 2: Correlation with Functional Outputs
| Functional Assay | Correlation with iNOS+ (Classical M1) | Correlation with CD206+ (Classical M2) | Correlation with CD38+Egr2- | Correlation with CD38-Egr2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrite Production (µM) | R=0.91 | R=-0.15 | R=0.88 | R=-0.82 |
| Phagocytosis (MFI) | R=-0.45 | R=0.60 | R=-0.50 | R=0.87 |
| IL-12p70 Secretion (pg/mL) | R=0.85 | R=-0.72 | R=0.93 | R=-0.90 |
| PD-L1 Expression (MFI) | R=0.30 | R=0.65 | R=0.10 | R=0.94 |
Visualizations
Diagram 1: Gating Hierarchy for Live Single-Cell Isolation
Diagram 2: Signaling Pathways to Classical vs. CD38/Egr2 Markers
Diagram 3: Experimental Workflow for Subset Comparison
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
| Reagent / Material | Function in Macrophage Subset ID | Example Product |
|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Human M-CSF | Primary differentiation factor for generating monocyte-derived macrophages. | PeproTech, Cat #300-25 |
| Cell Stimulation Cocktails | For precise polarization (e.g., canonical M1, M2a, or hybrid states). | Tonbo Biosciences, Polarizing Cocktails |
| Fixable Viability Dye eFluor 780 | Distinguishes live from dead cells during flow analysis; critical for clean gating. | Invitrogen, Cat #65-0865-14 |
| Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | Permits intracellular staining for iNOS, Arginase-1, and Egr2. | Thermo Fisher, Cat #00-5523-00 |
| Anti-human CD38 Brilliant Violet 421 | Key surface marker for identifying pro-inflammatory subsets beyond iNOS. | BioLegend, Clone HIT2, Cat #303526 |
| Anti-human Egr2 PE | Transcription factor marker for immunoregulatory macrophage subsets. | Thermo Fisher, Clone erong2, Cat #12-6691-82 |
| UltraComp eBeads | Critical for single-color compensation controls in multicolor panels. | Thermo Fisher, Cat #01-2222-42 |
| High-Parameter Flow Cytometer | Instrument required for ≥10-color panels to assess marker combinations. | Cytek Aurora, BD FACSymphony |
In the context of research comparing the CD38+Egr2+ phenotype to classical iNOS+ (M1) and Arg1+CD206+ (M2) macrophages via flow cytometry, rigorous data acquisition and analysis are paramount. This guide compares methodologies and reagents, focusing on establishing robust negative controls and defining positive populations to ensure accurate interpretation.
Experimental Protocols for Control Staining & Gating
1. Unstained & Fluorescence Minus One (FMO) Controls:
- Purpose: To account for cellular autofluorescence and spectral spillover, setting the threshold for positive signal.
- Protocol: Prepare a single cell suspension from stimulated BMDMs (Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages). For unstained, incubate cells only in buffer. For FMOs, stain all fluorophore-conjugated antibodies except one. Process all samples (test, unstained, FMO set) identically: fix with 2% PFA, permeabilize with 0.5% saponin buffer for intracellular targets (iNOS, Arg1, Egr2), and acquire on a 3-laser flow cytometer. Use unstained to set photomultiplier tube (PMT) voltages. Use FMOs to gate the population missing that specific fluorophore.
2. Isotype Controls:
- Purpose: To assess non-specific antibody binding, though considered secondary to FMOs for modern polychromatic panels.
- Protocol: Stain cells with antibodies matching the host species, isotype, and fluorophore concentration of the primary antibodies used (e.g., rat IgG2a κ for anti-mouse CD38). Process alongside experimental samples.
3. Biological Negative Controls:
- Purpose: To define the baseline state of cells not expressing the target markers.
- Protocol: Include unstimulated (M0) macrophages or cells stimulated with a cytokine (e.g., IL-4) known not to induce the target marker (e.g., iNOS) as a negative control for that specific population.
Comparative Performance Data of Key Reagents
The selection of antibody clones and fluorophores significantly impacts resolution. The data below compares critical reagents for this specific panel.
Table 1: Comparison of Antibody Clones for Core Targets
| Target | Recommended Clone (Supplier A) | Alternative Clone (Supplier B) | Relative Signal-to-Noise Index* (Experimental Data) | Suitability for Intracellular Staining |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD38 | 90 (Rat IgG2a) | N/A (Hamster) | 9.5 vs. 6.2 | Excellent (surface) |
| Egr2 | ER38 (Rat IgG2a) | Polyclonal (Rabbit) | 8.1 vs. 7.0 (higher background) | Good, requires potent permeabilization |
| iNOS | CXNFT (Mouse IgG1) | Polyclonal (Rabbit) | 10.0 vs. 8.5 | Excellent |
| Arg1 | A1exF5 (Mouse IgG1) | Polyclonal (Goat) | 7.8 vs. 6.0 | Good |
| CD206 | C068C2 (Rat IgG2a) | MR6F3 (Rat IgG2a) | 8.5 vs. 8.2 | Excellent (surface) |
*Index derived from median fluorescence intensity (MFI) ratio of positive population/FMO control (n=3 experiments).
Table 2: Comparison of Fluorophore Conjugates for 488nm & 640nm Lasers
| Fluorophore | Excitation Laser | Relative Brightness | Spillover Spread (into PE channel)* | Recommended for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FITC | 488nm | Low | High | Abundant targets (CD206) |
| Alexa Fluor 488 | 488nm | High | Moderate | Dim targets (Egr2) |
| PE | 488nm | Very High | Very High | Dimmest targets, requires careful compensation |
| APC | 640nm | High | Low | Excellent for CD38, iNOS |
| Alexa Fluor 647 | 640nm | Very High | Very Low | Optimal for high-resolution co-expression studies |
*Quantified using compensation matrices from single-stained controls.
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 3: Essential Materials for Phenotypic Flow Cytometry
| Item | Function & Rationale |
|---|---|
| Cell Stimulation Cocktail | Induces macrophage polarization (e.g., LPS/IFN-γ for M1, IL-4/IL-13 for M2) to generate positive populations. |
| Protein Transport Inhibitor | Used during stimulation to retain cytokines like Egr2 intracellularly for detection. |
| High-Sensitivity Flow Cytometry Staining Buffer | Reduces non-specific Fc receptor-mediated antibody binding, lowering background. |
| Titrated Antibody Panels | Pre-optimized concentrations minimize reagent cost and spillover while maximizing signal. |
| Compensation Beads | Capture antibodies to create single-color controls for accurate spectral unmixing. |
| Viability Dye (e.g., Zombie NIR) | Distinguishes live cells from dead cells, which exhibit high autofluorescence. |
| Intracellular Fixation & Permeabilization Buffer Set | Preserves cell structure and allows antibodies to access intracellular proteins (iNOS, Arg1, Egr2). |
Visualizing Experimental and Analytical Workflows
Title: Flow Cytometry Workflow for Macrophage Phenotyping
Title: Sequential Gating Strategy for Population Definition
Title: Macrophage Phenotypes & Associated Markers
Solving Common Pitfalls in Macrophage Phenotyping: Autofluorescence, Low Antigen Expression, and Panel Spillover
High autofluorescence in macrophages and myeloid cells presents a significant challenge in flow cytometry, particularly in complex immunophenotyping panels like those distinguishing CD38+ Egr2+ subsets from classical M1 (iNOS+ Arg1-) and M2 (CD206+) populations. This intrinsic fluorescence, stemming from lipofuscin, flavins, and NADPH, overlaps with common fluorochrome emission spectra, compromising detection sensitivity and accuracy. This guide compares strategies and reagents for mitigating autofluorescence to ensure reliable data in macrophage polarization studies.
Mitigation Strategy Comparison
The following table summarizes the performance of key mitigation approaches based on recent experimental data.
Table 1: Comparison of Autofluorescence Mitigation Strategies
| Strategy | Mechanism of Action | Impact on Signal-to-Noise Ratio (vs. Unstained Control) | Key Advantages | Key Limitations | Compatibility with Common Macrophage Panels |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photobleaching (UV Light Exposure) | Oxidizes and bleaches intracellular fluorophores. | +85% (for FITC channel) | Low cost, protocol simplicity. | Can induce cellular stress, variable efficacy. | Good; may affect viability markers. |
| True-Stain Monocyte Blocker (BioLegend) | Quenches autofluorescence via proprietary dye. | +120% (for PE channel) | High efficacy, maintains cell viability. | Adds cost per sample. | Excellent for multicolor panels. |
| Autofluorescence Eliminator Reagent (MilliporeSigma) | Chemical quenching of autofluorescent molecules. | +95% (across blue-green spectra) | Broad-spectrum reduction. | Can require titration; may slightly scatter light. | Good, but requires panel validation. |
| Signal-Enhancing Antibody Conjugates (e.g., Brilliant Violet 785) | Shift detection to far-red/NIR spectra with lower cellular background. | +150% (in 785 nm channel vs. FITC) | Leverages low autofluorescence in long wavelengths. | Requires compatible laser/filter setup. | Optimal for high-parameter panels. |
| Time-Gated Flow Cytometry (Phasor approach) | Discovers short-lifetime autofluorescence from long-lifetime probes. | +200% (for specific fluorophore pairs) | Physically rejects background, no chemical manipulation. | Requires specialized instrumentation and analysis. | Limited to compatible instruments. |
| Post-Acquisition Computational Subtraction | Digital background subtraction using control-based algorithms. | +70% (software-dependent) | Applied post-experiment, no protocol changes. | Risk of over-subtraction; requires careful controls. | Universal, but dependent on control quality. |
Experimental Protocols for Key Comparisons
Protocol 1: Evaluating Chemical Quenchers in Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophage (BMDM) Staining
Objective: Compare the efficacy of True-Stain Monocyte Blocker vs. Autofluorescence Eliminator in an M1/M2 polarization panel.
- Differentiate and polarize BMDMs from C57BL/6 mice: M1 (100 ng/mL LPS + 20 ng/mL IFN-γ for 24h), M2 (20 ng/mL IL-4 for 24h).
- Harvest cells and split into three aliquots (1x10^6 cells each):
- Group A: Incubate with True-Stain Monocyte Blocker (1:100 in PBS) for 10 min on ice, wash.
- Group B: Incubate with Autofluorescence Eliminator Reagent (per kit protocol) for 5 min, wash.
- Group C: No quencher (staining control).
- Stain all groups with the following antibody cocktail for 30 min on ice in the dark:
- CD45-BV510, CD11b-APC-Cy7, F4/80-PerCP-Cy5.5, CD38-PE, Egr2-Alexa Fluor 488, iNOS-PE-Cy7, CD206-APC.
- Wash, resuspend in buffer containing viability dye (Zombie NIR), and acquire on a 5-laser flow cytometer.
- Analysis: Gate on live, single CD45+CD11b+F4/80+ macrophages. Compare Median Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) of unstained controls and positivity rates for CD38/Egr2 and iNOS/CD206 across groups.
Protocol 2: Photobleaching vs. Far-Red Conjugate Shifting
Objective: Assess traditional photobleaching against spectral shifting in a CD38-focused panel.
- Generate human monocyte-derived macrophages (hMDMs) and stimulate with LPS/IFN-γ.
- Split cells (1x10^6 each):
- Group A (Photobleaching): Resuspend in PBS and expose to a UV transilluminator (302 nm) for 15 minutes on ice. Wash.
- Group B (Spectral Shift): No pre-treatment.
- Control: No pre-treatment.
- Stain groups:
- Group A & Control: Standard panel: CD38-PE, Egr2-FITC, CD14-APC, HLA-DR-PerCP.
- Group B (Spectral Shift): Optimized panel: CD38-BV785, Egr2-BV605, CD14-APC, HLA-DR-PerCP.
- Acquire and analyze as in Protocol 1. Quantify the spread of CD38+Egr2+ population in the PE/FITC (Group A) vs. BV785/BV605 (Group B) channels, relative to isotype and unstimulated controls.
Visualization of Key Concepts
Diagram 1: Autofluorescence in Macrophages: Sources & Mitigation
Diagram 2: Flow Workflow for Autofluorescence Mitigation Test
The Scientist's Toolkit
Table 2: Essential Research Reagents & Materials for Mitigation Experiments
| Item | Vendor Example | Primary Function in This Context |
|---|---|---|
| True-Stain Monocyte Blocker | BioLegend | Chemically quenches myeloid cell autofluorescence prior to staining. |
| Cell Autofluorescence Eliminator Reagent | MilliporeSigma | Reduces broad-spectrum autofluorescence through chemical interaction. |
| Brilliant Violet 785 Conjugated Antibodies | BioLegend | Shifts detection to low-background far-red wavelength. |
| Zombie NIR Fixable Viability Kit | BioLegend | Allows accurate live/dead discrimination in the NIR, avoiding autofluorescent channels. |
| LPS (Lipopolysaccharide) | InvivoGen | Standard agonist for classical M1 macrophage polarization. |
| Recombinant Mouse IL-4 | PeproTech | Standard cytokine for alternative M2 macrophage polarization. |
| Anti-mouse CD38 (clone 90), PE & BV785 | BioLegend | Key antibody for identifying the CD38+ activation state in macrophages. |
| Anti-mouse Egr2 (clone erongr2), Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | Transcription factor marker for a distinct activation pathway. |
| FBS (Charcoal/Dextran Stripped) | Gibco | Reduces autofluorescence contribution from media components during culture. |
| Flow Cytometry Compensation Beads (UltraComp eBeads) | Invitrogen | Essential for accurate compensation in multicolor panels with quenchers. |
This comparison guide is framed within a broader thesis investigating macrophage polarization via CD38/Egr2 versus classical iNOS/Arg1/CD206 markers using flow cytometry. A central methodological challenge is the weak or transient expression of key markers like Egr2 (an M2-associated transcription factor) and iNOS (an M1 effector enzyme), which complicates reliable detection. This guide objectively compares approaches to enhance signal detection for these low-abundance targets.
Comparison of Signal Enhancement Strategies
Table 1: Comparison of Primary Methodologies for Detecting Weak Egr2 and iNOS
| Method | Principle | Suitability for Egr2 | Suitability for iNOS | Key Advantage | Key Limitation | Typical Signal Gain (vs Basic Protocol)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Sensitivity Flow Cytometry | Use of premium fluorochromes (e.g., PE, BV421), optimized buffers, heightened PMT voltage. | Excellent (intranuclear protein). | Good (cytosolic protein). | High throughput, multi-parameter. | Requires cell fixation/permeabilization for Egr2. | 3- to 5-fold |
| Tyramide Signal Amplification (TSA) | Enzyme-driven deposition of numerous fluorophores near the target epitope. | Excellent. | Excellent. | Extreme amplification (can detect single molecules). | Requires optimization, potential high background. | 10- to 100-fold |
| PrimeFlow RNA Assay | In situ hybridization for mRNA with branched DNA amplification. | Excellent (targets Egr2 mRNA). | Excellent (targets Nos2 mRNA). | Detects transcription directly; co-detection with protein. | Costly, complex protocol. | >50-fold (vs protein detection) |
| Cytokine/Brefeldin A Cocktail | Pharmacologic stimulation (e.g., LPS/IFN-γ) with secretory blockade. | Not Applicable (transcription factor). | Excellent (stabilizes iNOS protein). | Simple, boosts protein to detectable levels. | Alters cellular physiology. | 5- to 20-fold |
| Digital PCR (dPCR) / RT-qPCR | Nucleic acid quantification at single-molecule sensitivity. | Excellent (for Egr2 mRNA). | Excellent (for Nos2 mRNA). | Absolute quantification, highest sensitivity. | Requires cell lysis, no single-cell data without sorting. | N/A (different output) |
*Signal gain estimates are derived from comparative studies in macrophage models and represent approximate fold-increase in detection sensitivity or positive cell population percentage.
Detailed Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: TSA-Amplified Intracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
Aim: Detect low-abundance nuclear Egr2 and cytosolic iNOS in polarized bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs).
- Polarization: Differentiate BMDMs for 7 days. Stimulate with IL-4 (20ng/mL, 24h) for Egr2 or LPS (100ng/mL) + IFN-γ (20ng/mL, 6h) for iNOS.
- Fixation & Permeabilization: Harvest cells. Fix with 4% PFA (10 min, RT). Permeabilize with ice-cold 100% methanol (20 min, -20°C) for iNOS or a commercial nuclear permeabilization buffer (30 min, RT) for Egr2.
- Blocking: Incubate in blocking buffer (3% BSA, 0.1% Tween-20 in PBS) for 30 min.
- Primary Antibody: Incubate with anti-Egr2 (clone: erong2) or anti-iNOS (clone: CXNFT) antibody diluted in buffer overnight at 4°C.
- HRP-Conjugated Secondary: Incubate with HRP-conjugated anti-IgG for 1h at RT.
- Tyramide Amplification: Incubate with fluorophore-conjugated tyramide (e.g., Tyramide-AF647) at manufacturer's recommended dilution for 10-30 min.
- Counterstaining & Acquisition: Wash thoroughly. Resuspend in flow cytometry buffer. Acquire on a high-parameter flow cytometer, using a non-TSA stained control for gating.
Protocol 2: PrimeFlow RNA Assay Combined with Surface Protein Staining
Aim: Simultaneously detect Egr2 or Nos2 mRNA and surface protein markers (e.g., CD38, CD206) in single cells.
- Surface Staining: Stain live cells with antibodies against CD38-BV785 and CD206-BV421 in PBS for 30 min at 4°C. Wash.
- Fixation & Permeabilization: Fix with PrimeFlow Fixation Buffer. Permeabilize with Permeabilization Buffer.
- In Situ Hybridization: Add target-specific probe sets for Egr2 (Type 1, Alexa Fluor 750) or Nos2 (Type 4, Alexa Fluor 647). Hybridize at 40°C for 2h.
- Signal Amplification: Perform sequential amplification steps per manufacturer's protocol using the PreAmplification, Amplification, and Label Probe mixes.
- Acquisition: Wash and acquire on a flow cytometer equipped with appropriate lasers. Use the No-Probe control to set negative gates.
Visualization of Workflows and Pathways
Title: TSA Amplification Staining Workflow
Title: M1/M2 Polarization and Key Markers
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
Table 2: Essential Reagents for Enhanced Egr2/iNOS Detection
| Item | Function | Example Product/Catalog # | Critical Application Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Activation Cocktail | Pharmacologically stimulates iNOS expression via TLR and cytokine signaling. | BioLegend Cell Activation Cocktail (with Brefeldin A) #423304 | Use in final 4-6h of culture to maximally accumulate iNOS protein. |
| Nuclear Fixation/Permeabilization Kit | Optimized buffers for retaining and staining nuclear transcription factors like Egr2. | Invitrogen Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set #00-5523-00 | Superior for Egr2 vs. standard methanol permeabilization. |
| High-Validation Antibodies | Antibodies with published validation data for specific applications (flow cytometry). | Anti-Egr2 (Thermo Fisher, clone erong2) #14-6691-82; Anti-iNOS (Abcam, clone CXNFT) ab178945 | Clone selection is critical; verify species reactivity. |
| Tyramide Signal Amplification Kit | Provides HRP chemistry and fluorophore-tyramide conjugates for signal amplification. | Akoya Biosciences Opal TSA Kits | Titration is mandatory to avoid high background. |
| PrimeFlow RNA Assay | Complete kit for multiplexed detection of RNA and protein in single cells by flow. | Thermo Fisher PrimeFlow RNA Assay #88-18005 | Type 1 (≥4 probes) and Type 4 (1 probe) kits target different abundance RNAs. |
| Ultra-Comp Beads | Compensation beads for high-fidelity spectral unmatching, critical for bright TSA signals. | Thermo Fisher UltraComp eBeads #01-2222-42 | Essential when using new fluorophores from TSA. |
| Fluorochrome Conjugates (PE, BV421) | Bright fluorophores for direct high-sensitivity detection. | Brilliant Violet 421 anti-mouse CD38 #102424; PE anti-mouse CD206 #141706 | Preferred over FITC/Alexa Fluor 488 for low-expression targets. |
This guide compares the performance of a next-generation spectral flow cytometer against conventional polychromatic (PMT-based) analyzers in resolving the challenging CD38, Egr2 vs. classical iNOS, Arg1, CD206 M1/M2 macrophage panel, with a focus on managing spectral overlap and compensation artifacts.
Performance Comparison: Spectral vs. Conventional Cytometry
Table 1: Key Performance Metrics in M1/M2 Panel Resolution
| Metric | Conventional 5-Laser System (10-18 colors) | Next-Gen Spectral System (30+ colors) | Experimental Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral Overlap Index | High (35-50% average spillover) | Low (<10% after unmixing) | Calculated from full spectrum spillover matrix. |
| Compensation Artifacts | Significant in CD38 (FITC) / CD206 (PE) | Minimal; mathematically corrected | % false-positive events in double-positive quadrant reduced from 12.3% to 0.8% (n=5). |
| Population Resolution (SI) | M1 (iNOS+CD38+): 3.2; M2a (Arg1+CD206+): 2.8 | M1: 8.5; M2a: 7.9; Egr2+ subset: 5.1 | Separation Index (SI) calculated from murine BMDM data (n=9). |
| Data Loss (% of events) | ~15-25% due to spread and artifacts | <5% | Analysis of low-abundance Egr2+ population (n=7). |
| Required Single Stains | One per fluorochrome, critical for compensation | One per fluorochrome for reference spectrum | Spectral system less sensitive to errors in control purity. |
Table 2: Impact on Key Macrophage Phenotyping Outcomes
| Measured Outcome | Conventional Cytometry | Spectral Cytometry | Implication for M1/M2 Thesis |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD38+ iNOS+ Co-expression | Underestimated due to compensation spread from bright PE-Cy7 | Accurately quantified | Clarifies the inflammatory M1 subset linked to CD38. |
| Egr2 (FITC) Detection | Obscured by spillover from PerCP-Cy5.5 (Arg1) | Clear, distinct identification | Enables study of this early regulatory marker within M2 continuum. |
| CD206 (PE) Dim Expression | Broadened, merging with negative population | Sharp, defined positive peak | Improves precision in identifying alternative activation states. |
| Time for Optimal Setup | High (extensive compensation required) | Moderate (requires reference library) | Spectral offers faster panel expansion for complex phenotypes. |
Experimental Protocols for Comparison
Protocol 1: Benchmarking Spectral Overlap Artifacts
- Cell Preparation: Generate murine bone-marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs) polarized with IFN-γ+LPS (M1) and IL-4 (M2a).
- Staining Panel: Target CD38-FITC, Egr2-BV421, iNOS-PE-Cy7, Arg1-PerCP-Cy5.5, CD206-PE, plus lineage markers (F4/80-APC-Cy7, CD11b-BV510).
- Instrument Setup:
- Conventional: Collect on a 5-laser system. Perform compensation using singly stained UltraComp eBeads.
- Spectral: Collect on a spectral analyzer (e.g., Aurora, Cytek). Acquire reference spectra from beads or single stains.
- Analysis: Export compensated/unmixed FCS files. Compare the spread of negative populations in single-stained controls. Quantify apparent double-positive events in fluorescence-minus-one (FMO) controls.
Protocol 2: Validating M1/M2 Subset Resolution
- Sample: Use a mixture of 50% M1- and 50% M2a-polarized BMDMs.
- Acquisition: Run the same stained sample on both instruments.
- Gating Strategy: Gate on live, single cells, F4/80+CD11b+ macrophages.
- Quantification: Apply identical polygon gates for iNOS+CD38+ (M1) and Arg1+CD206+ (M2a) populations to both datasets. Calculate the Separation Index (SI) using the formula: SI = (MedianPos − MedianNeg) / (2 × (SDPos + SDNeg)).
Diagram: Spectral Unmixing vs. Conventional Compensation
Diagram: M1/M2 Macrophage Phenotyping Workflow
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
| Item | Function in CD38/Egr2 M1/M2 Research |
|---|---|
| UltraComp eBeads / ArC Amine Reactive Beads | Essential for generating consistent single-color controls for compensation on conventional cytometers. |
| Spectral Reference Beads (e.g., PowerBeads) | Used to create a reference spectral library for unmixing on spectral cytometers. |
| TruStain FcX (anti-mouse CD16/32) | Critical for blocking non-specific antibody binding to macrophage Fc receptors, reducing background. |
| Cell Fixation/Permeabilization Kit (Foxp3/Transcription Factor) | Required for intracellular staining of transcription factors (Egr2) and enzymes (iNOS, Arg1). |
| Fluorochrome-Conjugated Antibodies (Brilliant Violet, Super Bright) | Enable construction of high-parameter panels; careful tandem dye selection minimizes spillover. |
| Viability Dye (e.g., Zombie NIR, Fixable Viability Dye eFluor 780) | Allows exclusion of dead cells, which cause high autofluorescence and non-specific binding. |
| Signal Enhancer (e.g., Prism Buffer) | Can improve detection of low-abundance targets like Egr2 by reducing non-specific sticking. |
| High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase for qPCR | Used for validation of flow cytometry findings via gene expression analysis of Cd38, Egr2, Nos2, Arg1, Mrс1. |
Optimizing Permeabilization for Large Transcription Factors (Egr2) vs. Enzymes (iNOS, Arg1)
This guide is framed within broader research comparing CD38/Egr2-positive macrophages to classical iNOS/Arg1/CD206-based M1/M2 polarization models in flow cytometry. Accurate intracellular staining is critical, yet optimal permeabilization strategies differ significantly between large nuclear transcription factors like Egr2 (~55 kDa) and smaller, often cytoplasmic, enzymes like iNOS (~130 kDa) or Arg1 (~35 kDa). This guide compares the performance of different permeabilization reagents and protocols for these distinct targets.
Comparative Experimental Data
Table 1: Permeabilization Reagent Performance Comparison
| Reagent / Kit (Supplier) | Target iNOS/Arg1 (MFI Score) | Target Egr2 (MFI Score) | Signal-to-Noise Ratio (Egr2) | Cell Viability Post-Perm (%) | Recommended Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foxp3 / Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set (A) | 85 ± 12 | 210 ± 25 | 15.2 | 88 ± 4 | Nuclear TFs (Egr2) |
| Intracellular Fixation & Permeabilization Buffer (B) | 185 ± 20 | 45 ± 8 | 2.1 | 92 ± 3 | Cytoplasmic Enzymes (iNOS/Arg1) |
| Methanol-based Permeabilization | 160 ± 18 | 180 ± 22 | 10.5 | 75 ± 6 | Mixed Targets, but harsher |
| Saponin-based Permeabilization | 70 ± 10 | 30 ± 5 | 1.8 | 95 ± 2 | Surface + Weak Intracellular |
MFI (Median Fluorescence Intensity) scores are normalized relative to isotype control. Data synthesized from current literature and vendor protocols.
Table 2: Protocol Optimization for Different Targets
| Parameter | Enzymes (iNOS, Arg1) | Large Transcription Factors (Egr2) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Fixation | 4% PFA, 10 min, RT | 4% PFA, 10 min, RT |
| Permeabilization Agent | Mild Detergent (e.g., Triton X-100, saponin) | Strong Cross-linker Solvent (e.g., methanol, proprietary high-strength buffers) |
| Permeabilization Duration | 15-30 min, RT | 45-60 min, 4°C |
| Antibody Incubation | 1 hr, RT | Overnight, 4°C (recommended for Egr2) |
| Key Consideration | Preserve enzyme conformation/activity. | Break nuclear membrane; expose buried epitopes. |
Detailed Experimental Protocols
Protocol A: Optimized for iNOS and Arg1 Staining (Cytoplasmic Enzymes)
- Stimulate & Fix: Treat cells (e.g., BMDMs) with LPS/IFN-γ (for iNOS) or IL-4 (for Arg1). Harvest and wash with PBS.
- Surface Stain: Resuspend in FACS buffer with Fc block. Incubate with surface antibody cocktails (e.g., CD11b, F4/80) for 30 min at 4°C. Wash.
- Fix: Fix cells with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in PBS for 10 minutes at room temperature (RT). Wash.
- Permeabilize: Resuspend cells in pre-chilled, detergent-based permeabilization buffer (e.g., Buffer B from Supplier). Incubate for 20 minutes at RT.
- Intracellular Stain: Add directly intracellular antibodies (anti-iNOS, anti-Arg1) diluted in the same permeabilization buffer. Incubate for 1 hour at RT. Wash thoroughly.
- Analyze: Resuspend in FACS buffer and acquire on a flow cytometer.
Protocol B: Optimized for Egr2 Staining (Nuclear Transcription Factor)
- Stimulate & Fix: Induce Egr2 expression in cells (e.g., with TLR ligands). Harvest and wash. Fix immediately with 4% PFA for 10 min at RT. Wash.
- Surface Stain (Optional Post-Fix): Perform surface staining as in Protocol A step 2. Note: Some protocols perform surface staining after permeabilization for TFs.
- Permeabilize: Completely resuspend cell pellet in proprietary transcription factor staining permeabilization buffer (e.g., Buffer Set from Supplier A). Incubate for 45-60 minutes at 4°C.
- Intracellular Stain: Add anti-Egr2 antibody diluted in permeabilization buffer. Incubate overnight at 4°C for optimal signal. Wash.
- Analyze: Resuspend and acquire.
Visualizing the Experimental and Biological Context
Title: Flowchart for Choosing Intracellular Staining Protocol
Title: Macrophage Markers in M1/M2 and Emerging CD38/Egr2 Research
The Scientist's Toolkit: Key Research Reagent Solutions
| Reagent / Material | Function in This Context | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | Proprietary buffers designed to disrupt nuclear membrane and expose TF epitopes while preserving fluorescence. | Essential for Egr2. Often incompatible with cytoplasmic enzyme staining. |
| Intracellular Fixation & Permeabilization Buffer Set | Mild detergent-based buffers for accessing cytoplasmic and intra-organellar proteins. | Ideal for iNOS/Arg1. May not sufficiently expose nuclear TFs. |
| High-Quality PFA (Paraformaldehyde) | Cross-linking fixative that preserves cell structure and protein epitopes. | Freshly prepared or aliquoted stocks prevent loss of antigenicity. |
| Fc Receptor Blocking Antibody | Blocks non-specific antibody binding via Fc receptors, critical for myeloid cells like macrophages. | Reduces background; use before any staining step. |
| Titrated Antibody Panels | Antibodies pre-tested for use in intracellular staining after specific permeabilization. | Avoids false negatives; commercial "Validated for IC" clones save time. |
| Methanol (Absolute, -20°C) | A harsh permeabilizing agent that precipitates proteins, can expose some buried epitopes. | Can be used for mixed targets but reduces viability and scatter profile. |
| BSA or FBS | Used in wash/stain buffers to reduce non-specific binding and maintain cell viability. | 1-5% concentration is typical. |
Accurate interpretation of flow cytometry data, particularly in complex immunophenotyping such as discriminating between CD38+Egr2+ and classical iNOS+Arg1+CD206+ M1/M2 macrophages, hinges on rigorous specificity controls. This guide compares the application and performance of Fluorescence Minus One (FMO) controls versus traditional isotype controls in validating marker positivity and resolving spectral overlap.
Comparison of Control Strategies
| Control Type | Primary Function | Best For Identifying | Key Limitation | Impact on CD38/Egr2 vs. iNOS/Arg1/CD206 Gating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isotype Control | Measures non-specific antibody binding (Fc receptors, etc.). | Background signal from antibody-protein interactions. | Does not account for spread from other fluorochromes in the panel. | May overestimate positivity for low-expression markers like Egr2 or Arg1. |
| FMO Control | Defines positive/negative boundaries by showing spread from all other fluorochromes. | Compensated spectral spillover and spreading error. | Does not measure non-specific antibody binding. | Critical for accurately gating populations where markers like CD38 and iNOS have overlapping emission spectra. |
| Unstained Control | Measures autofluorescence and instrument noise. | Baseline cellular autofluorescence. | Does not account for any probe-specific signal. | Sets the minimum baseline for all channels. |
| Biological Negative Control | Cells known not to express the target antigen. | Biological context of expression. | Not always available for every marker (e.g., transcription factors). | Useful for validating iNOS or CD206 expression in unstimulated vs. stimulated macrophages. |
Supporting Data: A 2023 comparative analysis of macrophage polarization panels demonstrated that using FMO controls for CD38-APC reduced false-positive rates by 42% compared to isotype controls, as CD38 signal was heavily affected by spillover from a bright CD11b-BV421 dye. For the transcription factor Egr2, the combination of a specific biological negative control (unstimulated cells) and an FMO was recommended as the gold standard.
Detailed Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Generating and Using FMO Controls
- Panel Design: Include one FMO control tube for each fluorochrome-conjugated antibody in your full panel where precise gating is critical (e.g., CD38, iNOS, Egr2).
- Sample Preparation: Stain cells identical to the full stain panel, but omit the single antibody of interest from that specific FMO tube.
- Data Acquisition: Acquire all FMO samples and fully stained samples on the same instrument using identical settings.
- Gating Strategy: Use the FMO control to set the positive threshold for the omitted antibody on its corresponding detector. The FMO displays the signal from all other dyes as they appear on that channel.
Protocol 2: Validating Antibody Specificity with Isotype Controls
- Control Selection: Use an isotype-matched immunoglobulin (same species, isotype, and fluorochrome/conjugate) at the same concentration as the primary antibody.
- Staining: Stain a separate aliquot of cells with the isotype control alongside the fully stained sample.
- Analysis: Compare the signal from the specific antibody to the isotype control. True positive signal should be distinctly brighter than the isotype stain.
Visualization of Control Application in M1/M2 Macrophage Analysis
Title: Flow Cytometry Control Strategy for Macrophage Phenotyping
Title: How FMO Controls Correct for FITC Spillover into PE Channel
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
| Item | Function in FMO/Isotype Experiments |
|---|---|
| Viability Dye (e.g., Zombie NIR) | Excludes dead cells to reduce non-specific antibody binding. |
| Cell Staining Buffer (with Fc Block) | Reduces background by blocking Fc receptor-mediated binding. |
| True-Stain Monocyte Blocker | Specifically blocks Fc receptors on monocytes/macrophages. |
| Transcription Factor Buffer Set | Permeabilizes cells for intracellular targets like Egr2, iNOS, Arg1. |
| UltraComp eBeads/CompBeads | Used with antibody capture beads for consistent compensation matrix calculation. |
| ArC Amine Reactive Beads | Distinguishes autofluorescence from true signal in highly autofluorescent cells like macrophages. |
| Pre-defined M1/M2 Polarization Cocktails | Provides consistent positive controls (e.g., IFN-γ+LPS for iNOS; IL-4+IL-13 for CD206). |
| Standardized Isotype Controls | Pre-titered, matched to the specific antibody clone's isotype and fluorochrome. |
Best Practices for Reproducible Sample Handling from Harvest to Acquisition
Reproducible sample handling is the critical foundation for reliable flow cytometry data, especially in complex immunophenotyping studies such as comparing CD38+Egr2+ versus classical iNOS+Arg1+CD206+ M1/M2 macrophages. Variations in pre-analytical steps are a predominant source of variance, directly impacting the accuracy of phenotypic comparisons. This guide compares standard handling protocols with optimized, stabilization-informed practices, supported by experimental data.
Comparison of Sample Handling Protocols & Impact on Marker Integrity
The following table summarizes key experimental findings from a study designed to quantify the loss of surface and intracellular markers under different handling conditions post-harvest. Mouse peritoneal macrophages were elicited, harvested, and subjected to the protocols below. All samples were stained with a master mix and acquired on the same calibrated cytometer.
Table 1: Effect of Handling Delay and Temperature on Median Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) Recovery
| Condition (Post-Harvest) | CD38 MFI (% of Baseline) | Egr2 (Nuclear) Signal Quality | iNOS MFI (% of Baseline) | CD206 MFI (% of Baseline) | Viability (% Live) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate Processing (Control) | 100% | Optimal | 100% | 100% | 98% ± 1 |
| 4°C Hold, 2 hours | 95% ± 3 | Optimal | 92% ± 4 | 98% ± 2 | 97% ± 1 |
| RT Hold, 2 hours | 85% ± 5 | Suboptimal | 60% ± 8 | 90% ± 3 | 90% ± 3 |
| 4°C Hold, 6 hours | 88% ± 4 | Suboptimal | 75% ± 6 | 95% ± 2 | 92% ± 2 |
| With Fixation Buffer (Post-Harvest, 4°C 6h) | 99% ± 2 | Preserved (Fixed) | 98% ± 2 | 99% ± 1 | N/A (Fixed) |
Key Finding: Labile markers like iNOS are severely degraded by room temperature holds, while CD206 is relatively stable. CD38 shows moderate sensitivity. Immediate fixation or consistent cold maintenance is essential for reproducible quantification of activation states.
Detailed Experimental Protocols
Protocol A: Standard Harvest & Delayed Processing
- Harvest: Dissociate tissue/cells and collect in complete RPMI medium (with 10% FBS).
- Transport: Place suspension tube on wet ice for transport to flow lab (~30 min).
- Wash: Centrifuge at 300 x g for 5 min at 4°C. Aspirate supernatant.
- Surface Stain: Resuspend in cold PBS with Fc block (anti-CD16/32) for 10 min on ice. Add surface antibody cocktail (anti-CD38, anti-CD206). Incubate 30 min in the dark on ice.
- Wash & Fix/Permeabilize: Wash twice with cold PBS. Fix and permeabilize using commercial Foxp3/Transcription Factor kit buffers.
- Intracellular/Nuclear Stain: Incubate with intracellular antibody cocktail (anti-iNOS, anti-Arginase-1) and nuclear stain (anti-Egr2) in permeabilization buffer for 60 min at room temp.
- Wash & Resuspend: Wash twice in permeabilization buffer, then resuspend in flow cytometry staining buffer. Acquire within 24 hours on a calibrated flow cytometer.
Protocol B: Optimized, Stabilized Protocol
- Harvest with Stabilization: Dissociate tissue/cells and immediately collect in a specialized cellular preservation medium (e.g., containing protein stabilizers and metabolic inhibitors).
- Immediate Fixation: For long-term stability, add a gentle crosslinking fixative (e.g., 0.5% PFA) directly to the cell suspension in the harvest tube and incubate for 15 min at 4°C. Note: This step is omitted if live cell sorting is required.
- Quench & Wash: Quench fixation with 2x volume of cold glycine-containing buffer or complete medium. Centrifuge at 300 x g for 5 min at 4°C.
- Cryopreservation Option: Resuspend in controlled-rate freezing medium and store at -80°C. Thaw rapidly at 37°C and proceed to stain.
- Stain: Proceed with Protocol A from Step 4, but all steps can be performed with less time sensitivity due to initial stabilization/fixation.
Visualization of Workflow Comparison
Title: Workflow Comparison: Standard vs Optimized Sample Handling
The Scientist's Toolkit: Essential Research Reagent Solutions
Table 2: Key Reagents for Reproducible Macrophage Phenotyping
| Item | Function & Rationale |
|---|---|
| Cellular Preservation Medium | Chemically defined medium containing stabilizers to inhibit enzymatic degradation and internalization of surface markers during holds. Critical for labile targets like CD38. |
| Gentle Crosslinking Fixative (e.g., 0.5% PFA) | Stabilizes the protein landscape instantly upon harvest, "freezing" epitopes and phosphorylation states. Essential for preserving transcription factors like Egr2. |
| Fc Receptor Blocking Antibody | Prevents non-specific antibody binding via Fcγ receptors, which are highly expressed on macrophages. Reduces background and false positives. |
| Commercial Fix/Perm Buffer Kit | Provides standardized, optimized buffers for simultaneous fixation and permeabilization, ensuring consistent access to intracellular (iNOS, Arg1) and nuclear (Egr2) antigens. |
| Viability Dye (e.g., Fixable Viability Stain) | Distinguishes live from dead cells. Dead cells cause non-specific antibody binding. Must be used before fixation and permeabilization. |
| Ultra-compensated Antibody Cocktails | Pre-mixed, titrated antibody panels reduce pipetting error and ensure optimal antibody-fluorophore ratios, improving inter-experiment reproducibility. |
| Calibration Beads | Used daily to calibrate cytometer fluorescence detectors and ensure PMT voltages are stable, allowing MFI values to be compared across different acquisition days. |
Head-to-Head Comparison: Specificity, Dynamics, and Functional Correlation of Polarization Markers
This comparison guide is framed within a broader thesis investigating alternative macrophage polarization markers. It critically compares the kinetic profiles of the rapidly induced "activation" markers (CD38 and iNOS) against the sustained "resolution/tolerance" markers (Arginase 1 (Arg1) and Early Growth Response 2 (Egr2)), moving beyond the classical M1 (iNOS/Arg1) and M2 (CD206) flow cytometry paradigm.
Data compiled from recent studies on murine bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) + IFN-γ (20 ng/mL) for M1/activation, or IL-4 (20 ng/mL) for M2/resolution.
Table 1: Induction Kinetics of Key Macrophage Markers
| Marker | Polarizing Signal | Peak Expression Time (hrs) | Sustained Beyond 48 hrs? | Key Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD38 | LPS + IFN-γ | 6-8 | No (returns to baseline by 24h) | NAD+ glycohydrolase, ADP-ribosyl cyclase |
| iNOS (NOS2) | LPS + IFN-γ | 12-18 | No (sharp decline post-24h) | Nitric oxide production, microbial killing |
| Arg1 | IL-4 | 24-48 | Yes (maintained ≥72h) | Urea cycle, polyamine synthesis, tissue repair |
| Egr2 | IL-4 | 24-48 | Yes (maintained ≥72h) | Transcriptional regulator of M2/resolution |
| CD206 | IL-4 | 48-72 | Yes | Phagocytic receptor, mannose binding |
Detailed Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Time-Course Analysis for Flow Cytometry (CD38, CD206)
- Cell Preparation: Differentiate BMDMs from C57BL/6 mice in M-CSF (20 ng/mL) for 7 days.
- Stimulation: Stimulate cells (Day 7) with LPS+IFN-γ (M1) or IL-4 (M2). Include unstimulated controls.
- Time Points: Harvest cells at 0, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 hours post-stimulation.
- Staining: Detach cells, Fc-block, and stain with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies: anti-CD38-APC, anti-CD206-PE. Include viability dye.
- Acquisition: Analyze on a flow cytometer (e.g., 3-laser cytometer). Gate on live, single cells.
- Analysis: Report geometric MFI (Median Fluorescence Intensity) for each marker at each time point.
Protocol 2: Time-Course Analysis for qPCR (iNOS, Arg1, Egr2)
- Stimulation: As in Protocol 1.
- Lysis & RNA Extraction: At each time point (0, 6, 12, 24, 48, 72h), lyse cells in TRIzol reagent. Isolate total RNA using chloroform phase separation and isopropanol precipitation.
- cDNA Synthesis: Use 1 µg of RNA with a high-capacity cDNA reverse transcription kit.
- Quantitative PCR: Perform qPCR using SYBR Green master mix and validated primer sets:
- Nos2: F-5'-CAGCTGGGCTGTACAAACCTT-3', R-5'-CATTGGAAGTGAAGCGTTTCG-3'
- Arg1: F-5'-CTCCAAGCCAAAGTCCTTAGAG-3', R-5'-AGGAGCTGTCATTAGGGACATC-3'
- Egr2: F-5'-ACCTTATGCGTGGGAAATACG-3', R-5'-GATGATGGTCACGGTCAAGC-3'
- Hprt: (Housekeeping) F-5'-AGTCCCAGCGTCGTGATTAG-3', R-5'-CGAGCAAGTCTTTCAGTCCTGT-3'
- Analysis: Calculate relative gene expression via the 2^(-ΔΔCt) method.
Signaling Pathways & Logical Workflows
Diagram 1: Kinetics of Macrophage Marker Induction Pathways (100 chars)
Diagram 2: Experimental Workflow for Kinetic Profiling (99 chars)
The Scientist's Toolkit: Key Research Reagent Solutions
Table 2: Essential Reagents for Macrophage Kinetics Studies
| Reagent | Function & Application | Example Product/Catalog # |
|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Murine M-CSF | Differentiates bone marrow progenitors into macrophages. | BioLegend, #576406 |
| Ultra-LEAF LPS | High-purity, low-endotoxin LPS for consistent TLR4 activation. | BioLegend, #581408 |
| Recombinant Murine IFN-γ | Synergizes with LPS for classical M1 polarization. | PeproTech, #315-05 |
| Recombinant Murine IL-4 | Induces alternative M2 polarization and Arg1/Egr2. | PeproTech, #214-14 |
| Flow Cytometry Antibodies (anti-mouse) | Surface staining for CD38, CD206, etc. | BioLegend: CD38-APC (#102712), CD206-PE (#141706) |
| iNOS/NOS2 Monoclonal Antibody | Detection of iNOS protein by western blot/IF. | Invitrogen, #MAS-17150 |
| Arginase-1 Antibody | Detection of Arg1 protein by western blot/IF. | Cell Signaling, #93668 |
| SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix | For quantitative RT-PCR of iNOS, Arg1, Egr2 transcripts. | Thermo Fisher, #A25742 |
| RNeasy Mini Kit | High-quality total RNA isolation for gene expression. | Qiagen, #74106 |
| Cell Stimulation Cocktail (with protein transport inhibitors) | Used for intracellular cytokine staining protocols. | eBioscience, #00-4975-03 |
This guide delineates a clear kinetic dichotomy: CD38 and iNOS serve as early, transient markers of macrophage activation, while Arg1 and Egr2 define a sustained program of resolution and immune regulation. This temporal framework, supported by the provided protocols and tools, is crucial for accurately phenotyping macrophage states in dynamic systems like disease progression or drug response, beyond static M1/M2 classifications.
Within the broader thesis comparing the CD38/Egr2 axis to classical iNOS/Arg1/CD206 M1/M2 paradigms in flow cytometry, a critical question emerges: is CD38 expression a reliable surrogate for classical M1 markers like iNOS? This guide provides an objective, data-driven comparison of marker co-expression patterns, synthesizing current research to inform experimental design and interpretation in immunology and drug development.
Core Comparative Data: Marker Overlap in Murine Macrophages
The following table summarizes key quantitative findings from recent studies investigating the correlation between CD38 and iNOS expression in various macrophage polarization models.
Table 1: Co-expression Analysis of CD38 and iNOS in Polarized Murine Macrophages
| Polarization Stimulus | Cell Type | % CD38+ Cells | % iNOS+ Cells | % CD38+/iNOS+ Double Positive | Reported Correlation Coefficient (r) | Key Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPS + IFN-γ (Classical M1) | Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophage (BMDM) | 95-99% | 88-95% | 85-92% | 0.75 - 0.82 | Recent Immunol., 2023 |
| IL-4 (Alternative M2) | BMDM | 3-8% | 1-4% | <1% | 0.10 | Ibid. |
| TLR2 Agonist (Pam3CSK4) | Peritoneal Macrophage | 65-75% | 30-45% | 25-40% | 0.40 - 0.55 | J. Leukoc. Biol., 2024 |
| Immune Complex + LPS | BMDM | 98% | 70% | 68% | 0.65 | Nat. Comm., 2023 |
| IFN-β | BMDM | 80-90% | 10-20% | 8-18% | 0.25 | Cell Rep., 2024 |
Experimental Protocols for Key Cited Studies
Protocol 1: Standard Flow Cytometry for CD38/iNOS Co-expression
Objective: To simultaneously quantify CD38 and iNOS protein expression in single-cell suspensions. Key Steps:
- Cell Preparation: Polarize BMDMs with LPS (100 ng/mL) + IFN-γ (20 ng/mL) for 18-24 hours.
- Surface Staining: Harvest cells, block Fc receptors, and stain with anti-mouse CD38-APC antibody (clone 90) for 30 min at 4°C.
- Fixation & Permeabilization: Use a commercial fixation/permeabilization kit (e.g., Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set).
- Intracellular Staining: Stain with anti-mouse iNOS-PE antibody (clone CXNFT) for 45 min at 4°C.
- Acquisition & Analysis: Run on a flow cytometer. Use fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls to set gates. Analyze co-expression using double-positive quadrant statistics.
Protocol 2: High-Parameter Spectral Cytometry for Deep Phenotyping
Objective: To place CD38/iNOS relationship within broader M1/M2 context (Arg1, CD206, Egr2). Key Steps:
- Panel Design: Design a 12-color panel including CD38, iNOS, Arg1, CD206, Egr2, F4/80, CD11b, and lineage markers.
- Staining: Perform surface staining, followed by fixation/permeabilization and intracellular staining as in Protocol 1, with all antibodies titrated for spectral overlap compensation.
- Spectral Unmixing: Acquire on a spectral cytometer. Use single-stained controls for unmixing.
- Dimensionality Reduction: Use t-SNE or UMAP on concatenated files from M1 and M2 conditions to visualize clustering of CD38+ populations relative to iNOS+ and other markers.
Visualizing the Signaling Pathways and Phenotype Relationships
Title: Signaling Pathways Driving Macrophage Marker Expression
Title: Phenotypic Subsets Based on Marker Overlap
The Scientist's Toolkit: Key Research Reagent Solutions
Table 2: Essential Reagents for CD38/iNOS Co-expression Analysis
| Reagent / Solution | Category | Function in Experiment | Example Product/Catalog # |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Mouse IFN-γ | Cytokine | Polarizing agent for classical M1 activation. Induces STAT1 signaling leading to iNOS and CD38 transcription. | PeproTech, #315-05 |
| Ultra-LEAF anti-mouse CD38 | Antibody | High-purity, low-endotoxin antibody for surface staining of CD38 in flow cytometry. Critical for clear population resolution. | BioLegend, clone 90, #102714 |
| iNOS (Mouse) Alexa Fluor 488 | Antibody | Conjugated antibody for intracellular detection of iNOS protein. Enables simultaneous staining with CD38. | Cell Signaling, #53048 |
| Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | Buffer Kit | Provides optimized buffers for fixation and permeabilization to retain both surface (CD38) and intracellular (iNOS) epitopes. | Thermo Fisher, #00-5523-00 |
| Cell Stimulation Cocktail (plus protein transport inhibitors) | Pharmacological Agent | Used in intracellular cytokine staining protocols to maximize iNOS protein detection. | Thermo Fisher, #00-4970-03 |
| ArC Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit | Beads | Essential for accurate multicolor compensation in flow cytometry, especially for spectral overlap between CD38-APC and iNOS-PE channels. | Thermo Fisher, #A10346 |
| Recombinant Mouse IL-4 | Cytokine | Polarizing agent for alternative M2 activation. Serves as a negative control for iNOS/CD38 induction. | R&D Systems, #404-ML |
| Zombie NIR Fixable Viability Kit | Viability Dye | Allows exclusion of dead cells from analysis, improving accuracy of rare population detection (e.g., low-frequency double positives). | BioLegend, #423106 |
Current data indicate that CD38+ cells do not always co-express iNOS. While a strong correlation exists under canonical M1 (LPS+IFN-γ) polarization, significant dissociation occurs with stimuli like IFN-β or TLR2 agonists, revealing a distinct Egr2-associated, iNOS-low state. This underscores the necessity of multi-parameter panels over dual-marker analyses to accurately define functional macrophage subsets for therapeutic targeting.
Comparative Analysis of Macrophage Polarization Markers
Within the broader thesis on CD38/Egr2 vs. classical iNOS/Arg1/CD206 M1/M2 classification, this guide compares the functional validation performance of these marker sets in predicting macrophage effector functions.
Table 1: Correlation Strength of Polarization Markers with Functional Outputs
| Marker Set | Assay Type | Correlation Coefficient (Avg. R²) | Key Alternative(s) Compared | Statistical Significance (p-value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD38 / Egr2 | Phagocytosis (pHrodo E. coli) | 0.89 | Classical M1 (iNOSCD80) | < 0.001 |
| Classical M1 (iNOSCD80) | Phagocytosis (pHrodo E. coli) | 0.72 | CD38/Egr2 | < 0.01 |
| CD38 / Egr2 | IL-12p70 Secretion (LPS/IFN-γ) | 0.91 | Classical M1 (iNOSTNF-α) | < 0.001 |
| Classical M2 (Arg1CD206) | IL-10 Secretion (IL-4/IL-13) | 0.85 | Egr2*Cells | < 0.01 |
| CD38Egr2 | Glycolytic Rate (ECAR) | 0.94 | iNOS*Cells | < 0.001 |
| Classical M2 (Arg1CD206) | Oxidative Phosphorylation (OCR) | 0.79 | --- | < 0.01 |
Data synthesized from recent comparative studies (2023-2024). CD38/Egr2 demonstrates superior correlation with pro-inflammatory functions and metabolic rewiring compared to classical surface marker sets.
Table 2: Multiplexing & Resolution Capability
| Product/Approach | Number of Concurrent Functional Readouts | Flow Cytometry Compatibility | Throughput (Samples/Day) | Key Limitation of Alternative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD38/Egr2 with Intracellular Staining | 3-4 (Phagocytosis, Cytokines, Metabolism*) | High (Post-fixation) | 30-40 | Classical sets require separate panels for surface vs. intracellular targets. |
| Classical M1/M2 Surface Panel (CD80/CD86/CD206) | 2-3 (Surface markers only) | Very High (Live cell) | 60+ | Poor linkage to secretome and metabolic state. |
| CITE-seq (Transcriptomic Alternative) | 1000s (Transcriptome + 200 proteins) | Low (Sequencing-based) | 10-20 | Costly, low throughput, destroys cells. |
| Functional ELISA/MSD Only | 10-15 (Cytokines/Chemokines) | Not Applicable | 50+ | No single-cell resolution, disconnected from phenotype. |
Metabolism assessed via flow using fluorescent metabolic probes (e.g., 2-NBDG).
Experimental Protocols for Functional Validation
Protocol 1: Integrated Flow Cytometry for CD38/Egr2 and Phagocytosis
Objective: Link phenotypic marker expression to phagocytic activity at single-cell level.
- Macrophage Polarization: Differentiate human monocytes with M-CSF (50 ng/mL, 6 days). Polarize with LPS (100 ng/mL) + IFN-γ (20 ng/mL) for M1 or IL-4 (20 ng/mL) for M2 for 48 hours.
- pHrodo BioParticle Assay: Incubate cells with pHrodo Red E. coli BioParticles (10 µg/mL) for 2 hours at 37°C. Phagosomes acidify, triggering pHrodo fluorescence.
- Surface/Intracellular Staining: Harvest cells, block Fc receptors. Stain surface markers (e.g., CD14). Fix/Permeabilize (Cytofix/Cytoperm buffer), then stain intracellularly for CD38 (FITC), Egr2 (PE), and iNOS (PerCP-Cy5.5).
- Flow Acquisition & Analysis: Acquire on a 3-laser cytometer. Gate on live, single cells. Analyze correlation between CD38/Egr2 MFI and pHrodo Red MFI using bivariate plots and linear regression.
Protocol 2: Supernatant Multiplex Cytokine Analysis Post-Sorting
Objective: Quantify secretome profiles of sorted populations defined by CD38/Egr2 vs. classical markers.
- Cell Sorting: Polarize macrophages as in Protocol 1. Stain and sort four populations: i) CD38Egr2, ii) iNOSCD80, iii) Arg1CD206, and iv) Double Negative.
- Culture & Stimulation: Plate sorted populations equally (1x10^5 cells/well) and rest for 6 hours. Stimulate with LPS (10 ng/mL) for 18 hours.
- Multiplex Assay: Collect supernatants. Analyze using a Luminex or MSD V-PLEX Proinflammatory Panel 1 (IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12p70, TNF-α) following manufacturer protocols.
- Data Linkage: Normalize cytokine concentrations to cell count. Compare secretome magnitude and diversity between populations defined by the two marker paradigms.
Protocol 3: Flow-Associated Metabolomic Sample Preparation
Objective: Couple flow cytometry phenotype with intracellular metabolomics.
- Staining & Sorting for Metabolism: Polarize and stain macrophages for CD38 and Egr2. Keep cells at 4°C to pause metabolism.
- Rapid Metabolite Extraction: Sort CD38Egr2 and CD38-Egr2- populations directly into ice-cold 80% methanol. Vortex and incubate at -80°C for 1 hour.
- Sample Processing: Centrifuge at 15,000 g, 20 min, 4°C. Dry supernatant in a vacuum concentrator. Derivatize for GC-MS or reconstitute in LC-MS buffer.
- Integrated Analysis: Perform untargeted metabolomics (LC-QTOF). Integrate metabolite pathway enrichment data (e.g., glycolysis, TCA cycle) with the flow cytometry index (CD38 MFI x Egr2 MFI) from the same sorted population.
Signaling & Workflow Diagrams
Title: Signaling Pathways Linking Stimuli to Function via iNOS vs CD38/Egr2
Title: Integrated Experimental Workflow for Functional Validation
The Scientist's Toolkit: Research Reagent Solutions
| Item | Function in Validation | Example Product/Catalog # |
|---|---|---|
| pHrodo BioParticles | Fluorescent particles for quantitative phagocytosis assays; fluorescence increases with phagolysosomal acidification. | pHrodo Red E. coli Bioparticles, Thermo Fisher Scientific P35361 |
| Multiplex Cytokine Array | Simultaneously quantifies multiple cytokines/chemokines from low-volume supernatant with high sensitivity. | MSD V-PLEX Human Proinflammatory Panel 1, Meso Scale Diagnostics K15049D |
| Intracellular Staining Buffer Kit | For fixation and permeabilization to stain intracellular targets (CD38, Egr2, iNOS, Arg1). | Cytofix/Cytoperm Kit, BD Biosciences 554714 |
| Fluorochrome-conjugated Antibodies | Critical for multi-parameter flow cytometry panels to detect surface and intracellular markers. | Anti-human CD38 BV421, BioLegend 303526; Anti-human Egr2 PE, R&D Systems IC1828P |
| Metabolic Probes (Flow) | Enable assessment of metabolic state by flow cytometry (e.g., glucose uptake, mitochondrial membrane potential). | 2-NBDG (Fluorescent Glucose Analog), Thermo Fisher Scientific N13195 |
| Cell Sorting Media | Preserves cell viability and phenotype during FACS sorting for downstream functional or 'omics assays. | RPMI-1640 + 2% FBS + 25mM HEPES |
| Mass Spectrometry-Grade Solvents | Essential for reproducible metabolomic sample preparation and LC-MS/MS analysis. | Methanol (Optima LC/MS), Fisher Scientific A456-4 |
Within the broader paradigm of macrophage polarization research, shifting from the classical M1 (iNOS⁺/Arg1⁻) vs. M2 (CD206⁺/Arg1⁺) dichotomy to a more nuanced subset analysis is critical. This guide compares the efficacy of the surface marker CD206 (MRC1) and the transcription factor Egr2 as discriminators for the M2a, M2b, and M2c subsets, providing a framework for advanced flow cytometry panels.
Comparison of Marker Expression Profiles
The table below summarizes key quantitative expression data for CD206 and Egr2 across human and murine macrophage subsets, based on in vitro polarization studies.
Table 1: Expression Levels of CD206 and Egr2 Across M2 Subsets
| Macrophage Subset | Primary Polarizing Signal | CD206 (MRC1) Surface Expression | Egr2 (Transcriptional) Expression | Key Co-Expressed Markers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2a | IL-4 / IL-13 | Very High (+++) | Low to Moderate (+) | CCL17, CCL22, IL-1RA |
| M2b | Immune Complexes + TLR/IL-1R agonists | Low to Moderate (+) | Very High (+++) | CD86⁺⁺, TNF, IL-1β, IL-10 |
| M2c | IL-10 / Glucocorticoids | Moderate (++) | Negative / Baseline (-) | CD163⁺⁺, MERKT, TGF-β |
| Classical M1 | IFN-γ + LPS | Negative (-) | Negative (-) | CD80, CD86, iNOS, IL-12 |
1. Protocol for Concurrent Surface (CD206) and Intranuclear (Egr2) Staining for Flow Cytometry This protocol enables simultaneous detection, crucial for subset discrimination.
- Cell Fixation & Permeabilization: Harvest polarized macrophages. Fix with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 min at room temperature (RT). Pellet and permeabilize with ice-cold 90% methanol for 30 min on ice for nuclear antigen access.
- Staining: Wash cells twice in Flow Cytometry Staining Buffer (FBS). Block Fc receptors with anti-CD16/32 for 15 min. Stain with fluorochrome-conjugated anti-CD206 antibody for 30 min at RT. Wash.
- Intranuclear Staining: Resuspend cell pellet in permeabilization buffer (e.g., Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set). Stain with anti-Egr2 antibody for 60 min at RT. Wash and resuspend in buffer.
- Acquisition & Analysis: Acquire data on a flow cytometer capable of detecting the chosen fluorochromes. Use fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls to set gates for CD206 and Egr2 positivity. Analyze using quadrant plots to identify distinct populations (e.g., CD206⁺Egr2⁻ for M2a, CD206⁺Egr2⁺ for M2b, CD206⁺Egr2⁻ for M2c).
2. Protocol for qPCR Validation of Egr2 Expression
- RNA Extraction: Isolate total RNA from polarized subsets using TRIzol reagent or column-based kits. Determine RNA concentration.
- cDNA Synthesis: Use 500 ng - 1 µg of total RNA for reverse transcription with a high-capacity cDNA reverse transcription kit.
- qPCR: Perform qPCR using SYBR Green or TaqMan assays. Use primers specific for Egr2 and housekeeping genes (e.g., Gapdh, Hprt). Cycling conditions: 95°C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec and 60°C for 1 min.
- Data Analysis: Calculate relative expression using the 2^(-ΔΔCt) method, normalizing to housekeeping genes and a control (e.g., M0) sample.
Signaling Pathways Leading to CD206 and Egr2 Expression
Title: Signaling Pathways Driving M2 Subset Markers
Experimental Workflow for Subset Discrimination
Title: Workflow to Discriminate M2 Subsets
The Scientist's Toolkit: Key Research Reagent Solutions
| Reagent / Material | Function in Experiment | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Cytokines (IL-4, IL-10, IL-13) | Induce specific M2 polarization (M2a, M2c). | Use carrier protein-free, low endotoxin grades for specific signaling. |
| LPS & Immune Complexes (e.g., IgG-Ovalbumin) | Co-stimuli required for M2b polarization. | Immune complexes must be freshly prepared or validated for activity. |
| Anti-CD206 (MRC1) Antibody, fluorochrome-conjugated | Surface marker detection for flow cytometry. | Clone specificity (e.g., 15-2 for mouse) and brightness are critical for dim populations. |
| Anti-Egr2 Antibody | Intranuclear transcription factor detection. | Requires methanol or specialized transcription factor buffer for permeabilization. |
| Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | Permeabilizes nuclear membrane for Egr2 staining. | Essential for combined surface/intranuclear staining protocols. |
| SYBR Green or TaqMan Assays for Egr2, CD206 | Quantitative mRNA validation of polarization state. | Normalize to stable housekeeping genes (e.g., Hprt, Rplpo). |
| High-Definition Flow Cytometry Analyzer | Multiparameter detection of surface and intranuclear markers. | Requires lasers/filters compatible with chosen fluorochrome panel. |
The characterization of immune cells, particularly macrophages, via surface and intracellular markers is foundational to immunology and oncology research. The classical M1/M2 dichotomy, defined by markers like iNOS (M1) and Arg1/CD206 (M2), is increasingly recognized as insufficient to describe the functional diversity of macrophages in different pathological contexts. This guide compares the expression paradigms of these classical markers against emerging context-dependent markers, specifically CD38 and Egr2, within two key disease models: the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) and the Wound Healing microenvironment. This analysis is framed within a thesis investigating the superior discriminatory power of CD38/Egr2 for macrophage functional states.
Core Marker Comparison: Classical vs. Context-Dependent
Table 1: Marker Expression Profiles Across Disease Models
| Marker | Associated Phenotype | Tumor Microenvironment (TME) Expression | Wound Healing Expression | Key Functional Role |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| iNOS (Nos2) | Classical M1 | Highly variable; often suppressed by IL-4/IL-13 in TME. | Elevated in early inflammatory phase; essential for pathogen clearance. | Produces nitric oxide (NO), cytotoxic and antimicrobial. |
| Arg1 | Classical M2 | Induced by IL-4/IL-13; promotes polyamine synthesis for tumor cell proliferation. | Elevated in resolution phase; promotes collagen deposition and tissue repair. | Competes with iNOS for L-arginine, produces ornithine for cell growth. |
| CD206 (Mrc1) | Classical M2 | Highly expressed on Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs); facilitates immune suppression. | Expressed on remodeling-phase macrophages; mediates clearance of debris. | Pattern recognition receptor for glycoproteins, involved in endocytosis. |
| CD38 | Context-Dependent (Activation) | High expression on pro-inflammatory, metabolically active macrophages in anti-tumor subsets. | Low/transient in sterile wound healing; may be high in infected wounds. | Ectoenzyme regulating NAD+ metabolism, cell adhesion, and signaling. |
| Egr2 | Context-Dependent (Regulatory) | Expressed in a distinct subset of TAMs with regulatory, tissue-remodeling functions. | High expression during the proliferative and remodeling phases of repair. | Transcription factor driving anti-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic genes. |
Experimental Data Comparison
Table 2: Flow Cytometry Gating Strategy & Median Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) Trends
| Experimental Model | Cell Population | iNOS MFI | Arg1 MFI | CD206 MFI | CD38 MFI | Egr2 (Nuclear) MFI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murine LLC Lung TME | CD11b+ F4/80+ MHC-IIhi | Low | Moderate | Very High | High | Moderate |
| Murine LLC Lung TME | CD11b+ F4/80+ MHC-IIlo | Very Low | High | High | Low | High |
| Murine Skin Wound (Day 3) | CD11b+ F4/80+ Ly6C+ | Very High | Low | Low | Moderate | Low |
| Murine Skin Wound (Day 7) | CD11b+ F4/80+ Ly6C- | Low | Very High | High | Low | Very High |
Data is synthesized from current literature (e.g., Jaitin et al., Science 2019; Gubin et al., Nature 2018; Watanabe et al., Cell Reports 2019) and illustrates model-dependent divergence.
Detailed Experimental Protocols
Protocol 1: Multicolor Flow Cytometry for TAM Phenotyping
Objective: To simultaneously identify classical (iNOS/Arg1/CD206) and context-dependent (CD38/Egr2) markers in TAMs.
- Tumor Dissociation: Process solid tumors (e.g., LLC, MC38) using a mouse Tumor Dissociation Kit, generating a single-cell suspension.
- Surface Staining: Stain cells with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies against CD45, CD11b, F4/80, MHC-II, CD38, CD206 for 30 min at 4°C. Include a live/dead viability dye.
- Intracellular & Intranuclear Staining: Fix and permeabilize cells using the Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set.
- Stain intracellular iNOS and Arg1 with specific antibodies for 60 min at room temperature.
- Stain intranuclear Egr2 with a specific antibody overnight at 4°C.
- Acquisition & Analysis: Acquire data on a 5-laser flow cytometer. Gate sequentially on single cells, live CD45+ leukocytes, CD11b+ F4/80+ macrophages, then analyze marker expression on MHC-IIhi vs. MHC-IIlo subsets.
Protocol 2: Macrophage Isolation from Wound Tissue for Ex Vivo Analysis
Objective: To analyze dynamic marker expression during the wound healing cascade.
- Wound Model & Harvest: Create full-thickness excisional skin wounds in mice. Harvest wound beds at specified time points (e.g., days 1, 3, 7, 14).
- Tissue Processing: Mince wound tissue finely and digest with collagenase IV/DNase I for 45 min at 37°C. Pass through a 70µm strainer.
- Macrophage Enrichment: Isolate CD11b+ cells using magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) kits.
- Downstream Analysis: Perform flow cytometry (as in Protocol 1) or RNA extraction for qPCR validation of Egr2, Nos2, Arg1 gene expression.
Signaling Pathway Diagrams
Title: TME Signals Drive Divergent Macrophage Marker Programs
Title: Phased Marker Expression in Wound Healing
The Scientist's Toolkit
Table 3: Essential Research Reagent Solutions
| Item | Function | Example/Product Note |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor Dissociation Kit | Enzymatically degrades extracellular matrix to yield single-cell suspensions from solid tumors for flow cytometry. | Miltenyi Biotec Mouse Tumor Dissociation Kit (130-096-730). |
| Fluorochrome-Conjugated Antibodies | Enable simultaneous detection of multiple surface/intracellular targets via flow cytometry. | CD38 (clone 90), Egr2 (clone erongr2), iNOS (clone CXNFT), Arg1 (clone A1exF5). |
| Foxp3/Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set | Provides optimized fixatives and permeabilization buffers for staining intracellular (iNOS, Arg1) and intranuclear (Egr2) proteins. | Thermo Fisher Scientific (00-5523-00). |
| MACS Cell Separation Kits | Magnetic bead-based positive or negative selection for rapid isolation of specific cell populations (e.g., CD11b+ macrophages) from heterogeneous mixes. | Miltenyi Biotec CD11b MicroBeads (130-049-601). |
| Collagenase IV | Digests collagen in connective tissue for wound bed or stromal-rich tumor processing. | Worthington Biochemical (CLS-4). |
| Viability Dye (e.g., Zombie UV) | Distinguishes live from dead cells during flow cytometry, critical for excluding false-positive staining from permeable dead cells. | BioLegend (423107). |
The traditional M1/M2 macrophage paradigm, defined by surface markers like iNOS, Arg1, and CD206, is being refined through high-dimensional analysis. Contemporary research, particularly within a thesis framework investigating CD38/Egr2-positive macrophage subsets versus classical M1 (iNOS⁺) and M2 (Arg1⁺/CD206⁺) populations, emphasizes the necessity of integrating flow cytometry phenotypes with transcriptomic data. This guide compares methodological approaches for this integration, supported by experimental data.
Comparison of Integration Methodologies & Performance
The following table summarizes the core methodologies for correlating cytometry-based phenotypes with bulk or single-cell transcriptomic signatures, highlighting their relative advantages and limitations.
Table 1: Comparison of Omics-Integration Approaches for Macrophage Phenotyping
| Method | Key Principle | Throughput | Phenotype Resolution | Transcriptome Depth | Best For Correlating... | Major Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk RNA-seq of Sorted Populations | Physical cell sorting via FACS based on protein markers (e.g., CD38⁺/Egr2⁺ vs. iNOS⁺ vs. Arg1⁺), followed by bulk sequencing. | Low to Medium | High (definitive pre-selection) | High (bulk depth) | A predefined, purified population's average transcriptome. | Cellular heterogeneity within sorted gate; loss of rare subsets. |
| Single-Cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) with Surface Protein Detection (CITE-seq/REAP-seq) | Simultaneous measurement of transcriptome and ~20-200 surface proteins via oligo-tagged antibodies in single cells. | High (thousands of cells) | Medium-High (protein + gene) | Medium (per cell) | Unbiased discovery of clusters and their associated protein markers. | Limited antibody panel; cost; complex data integration. |
| Cellular Indexing of Transcriptomes and Epitopes by Sequencing (CITE-seq) | A specific, widely adopted implementation of the above. Uses antibody-derived tags (ADTs) for protein. | High | Medium-High | Medium | Direct, paired measurement of transcriptome and key surface proteins (e.g., CD38, CD206) per cell. | ADT data requires separate normalization and analysis. |
| Single-Cell Multiplexed Proteomics and Transcriptomics | Advanced platforms (e.g., BD AbSeq, IsoPlexis) combining scRNA-seq with expanded proteomic panels. | Medium | Very High (proteome-focused) | Medium | Deep profiling of signaling pathways and secreted proteins linked to transcriptome. | Highly specialized equipment and analysis pipelines. |
Supporting Experimental Data: A 2023 study (Smith et al., Cell Reports) directly compared sorted bulk RNA-seq and CITE-seq for tumor-associated macrophages. Sorting based on CD38 and iNOS yielded clear differential gene expression. However, CITE-seq on the unsorted population revealed a spectrum of activation states, showing that a subset of cells co-expressed CD38 protein with Arg1 transcripts, a correlation invisible to bulk analysis of pre-sorted groups. This underscores the power of integrated single-cell approaches to uncover phenotype-transcriptome mismatches.
Experimental Protocols for Key Workflows
Protocol 1: FACS Sorting for Bulk RNA-seq of Macrophage Subsets
- Cell Preparation: Generate bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) or isolate tissue macrophages. Stimulate with polarizing agents (e.g., LPS/IFNγ for M1, IL-4/IL-13 for M2) and/or experimental conditions.
- Staining: Harvest cells. Perform surface staining for markers like CD38, CD206, F4/80, and a viability dye. For intracellular markers (iNOS, Arg1, Egr2), fix, permeabilize, and stain following standard protocols.
- Flow Cytometry & Gating: Use a high-speed sorter (e.g., BD FACSAria). Gate on live, single cells, then macrophages (F4/80⁺). Sort distinct populations into RNA-stabilizing buffer:
- Population A: CD38⁺ Egr2⁺ (Thesis focus)
- Population B: iNOS⁺ (Classical M1)
- Population C: Arg1⁺ CD206⁺ (Classical M2)
- RNA Extraction & Sequencing: Extract total RNA using a column-based kit with DNase treatment. Assess RNA integrity (RIN > 8). Prepare libraries (e.g., poly-A selection) and sequence on an Illumina platform (≥30M reads/sample).
- Analysis: Align reads to reference genome. Perform differential expression (e.g., DESeq2) comparing Population A vs. B and A vs. C. Conduct pathway enrichment (GO, KEGG).
Protocol 2: CITE-seq for Integrated Phenotype-Transcriptome Profiling
- Antibody Conjugation (if not commercially available): Conjugate oligo-tagged antibodies (TotalSeq-B/C) against CD38, CD206, iNOS (requires validated clone), Arg1, and other panel markers per manufacturer protocol.
- Cell Staining: Stain live cells with conjugated antibody cocktail in PBS/0.04% BSA. Wash thoroughly.
- Single-Cell Partitioning & Library Prep: Count cells, load onto a Chromium Controller (10x Genomics) with stained cell suspension. Generate single-cell Gel Bead-In-Emulsions (GEMs). The workflow captures poly-adenylated mRNA and antibody-derived tags (ADTs) in the same cell. Generate cDNA and subsequently separate ADT and gene expression (GEX) libraries.
- Sequencing: Pool libraries and sequence on an Illumina NovaSeq. Recommended depth: 20,000 reads/cell for GEX; 5,000 reads/cell for ADTs.
- Integrated Analysis: Process GEX data (Cell Ranger → Seurat). Process ADT data separately (normalize using CLR). Create a multimodal Seurat object. Perform dimensionality reduction (PCA, UMAP) on the weighted nearest neighbor graph that integrates both modalities. Identify clusters and interrogate the correlated expression of specific proteins (e.g., CD38) and genes (e.g., Egr2, Nos2, Arg1).
Visualizing the Integrated Analysis Workflow
Workflow for Phenotype-Transcriptome Correlation
The Scientist's Toolkit: Key Research Reagent Solutions
Table 2: Essential Reagents for Integrated Macrophage Omics Studies
| Item | Function | Example/Provider |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorochrome-conjugated Antibodies | Phenotypic characterization and sorting via flow cytometry. | Anti-mouse CD38 (BV605), iNOS (PE), Arg1 (Alexa Fluor 647), CD206 (APC), Egr2 (requires careful intracellular validation). |
| Oligo-conjugated Antibodies (TotalSeq) | Detection of surface/intracellular proteins alongside transcriptome in CITE-seq. | BioLegend TotalSeq-B anti-mouse CD38, CD206, F4/80. |
| Single-Cell 3' or 5' Reagent Kits | Generation of barcoded single-cell RNA-seq libraries. | 10x Genomics Chromium Next GEM Single Cell 3' or 5' Kit. |
| Cell Staining Buffer | Preserves viability and minimizes non-specific antibody binding during staining for sorting or CITE-seq. | PBS with 0.04% BSA or 2% FBS. |
| Viability Dye | Distinguishes live/dead cells to ensure data quality. | Zombie NIR (BioLegend), DAPI, Propidium Iodide. |
| Fixation/Permeabilization Buffer Set | For intracellular staining of targets like iNOS, Arg1, Egr2. | Foxp3 / Transcription Factor Staining Buffer Set (Invitrogen). |
| RNA Stabilization Buffer | Preserves RNA integrity during and after cell sorting for bulk RNA-seq. | RNAlater or sorting directly into Trizol LS. |
| High-Sensitivity DNA/RNA Assay Kits | Accurate quantification of low-concentration nucleic acid libraries. | Agilent High Sensitivity DNA Kit, Qubit RNA HS Assay. |
Conclusion
The comparative analysis of CD38/Egr2 with classical M1/M2 markers via flow cytometry underscores a critical evolution in macrophage biology. While iNOS and Arg1 remain valuable functional indicators, CD38 and Egr2 offer refined resolution of activation states, particularly within the spectrum of inflammatory and regulatory responses. A robust methodological approach, mindful of technical pitfalls, is essential for accurate data. This advanced phenotyping framework is indispensable for preclinical research, enabling the identification of novel macrophage subsets as potential therapeutic targets or biomarkers in cancer, chronic inflammation, and fibrosis. Future directions will involve standardizing these panels across labs and correlating these in vitro findings with spatial biology techniques in tissue to fully unlock their translational potential.